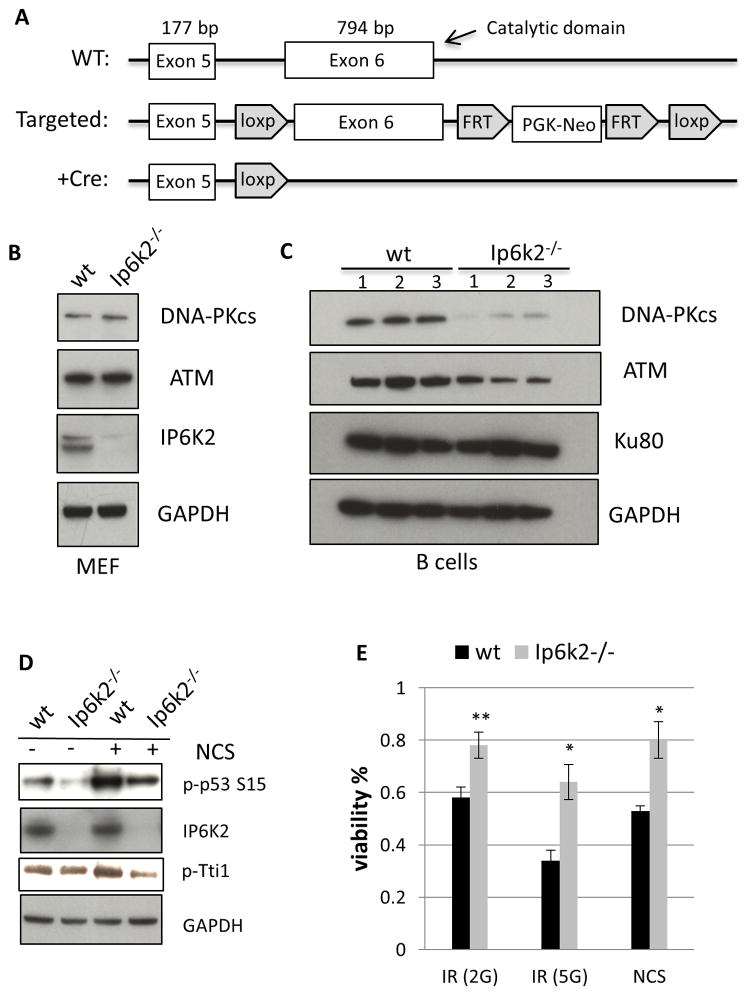
Figure 5.
IP6K2 mediates the DNA-PKcs/ATM-p53 pathway in murine B cells. (A) Schematic depiction of the targeting strategy used to generate Ip6k2−/− mice. Exon 6, containing the majority of the catalytic domain and the 3′ UTR, was flanked by loxP sites to generate the Flox/Flox mice. Breading with a Cre driver mice leads to targeted deletion of exon 6 and loss of IP6K2 expression. (B) Western-blot analysis of primary MEFs prepared from littermate wildtype and Ip6k2−/− mice. (C) Western-blot analysis of resting B cells prepared from littermate wildtype and Ip6k2−/− mice. (D) Western-blot analysis of resting B cells treated with or without NCS (20 μM, 1 h). (E) Viability of B cells after treatment with ionizing radiation (2G, 5 G) or NCS (40 μM). see also Figure S5.