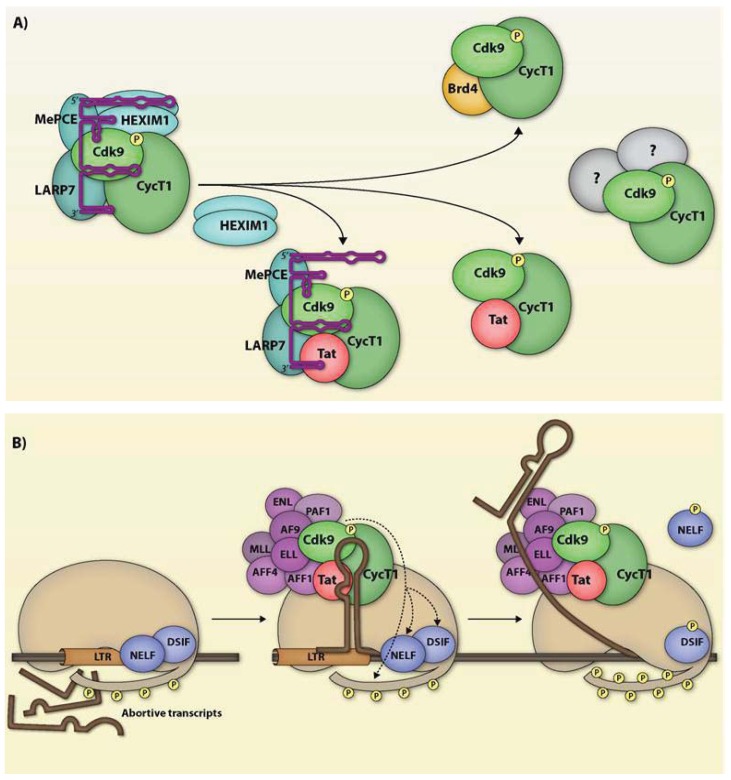
Figure 2.
P-TEFb complexes. (A) Inactive P-TEFb is sequestered in the 7SK snRNP. Brd4 and Tat can both recruit P-TEFb directly from the inactive complex for cellular or HIV-1 transcription, respectively. Tat has also been found to associate with 7SK snRNP lacking the HEXIM dimers, hypothesized to be an intermediate of the P-TEFb recruitment process. Recently, P-TEFb has been shown to immunoprecipitate with a number of additional proteins, although the functional relevance of these associations has yet to be determined; (B) Prior to P-TEFb recruitment, proviral transcription proceeds inefficiently, resulting in the production of abortive transcripts. RNAP II processivity is highly increased following Tat-mediated recruitment of P-TEFb to the TAR RNA, where it also associates with the SEC. Cdk9 phosphorylates the negative elongation factors NELF and DSIF, resulting in the dissociation of NELF and the conversion of DSIF into a positive elongation factor, and the Ser2 residues of the RNAP II CTD, inducing efficient transcriptional elongation.