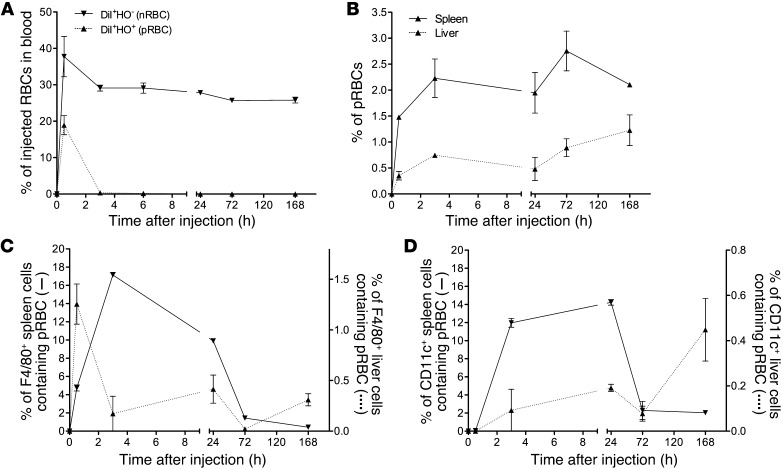
Figure 2. Tracking of attenuated parasites stained with DiI and HO. rbcs from a P. chabaudi–infected mouse (parasitemia, 39.8%; Supplemental Figure 5A) were treated with centanamycin, stained with DiI and HO, and then injected i.v. into naive AJ mice (3 mice, 5 × 107 cells per mouse). rbcs from an uninfected mouse were stained with DiI alone and injected into other mice (3 mice, 5 × 107 cells per mouse).
DiI+HO– cells (nrbcs) or DiI+HO+ cells (prbcs) in the peripheral blood of recipient mice were analyzed over time by flow cytometry and the percentage of these cells of the total injected nrbcs or prbcs calculated based on an assumption of the recipient mice each containing a total of 5 × 109 rbcs (A). Spleen and liver cells of recipient mice were prepared by mechanical disruption. rbcs were gated and DiI+HO+ cells identified. The percentages of DiI+HO+ cells of the total rbcs in the spleen and liver were then calculated (B). Free rbcs were then lysed using NH4Cl-Tris buffer to allow estimation of rbc uptake by white cells. Percentages of DiI+HO+F4/80+ or DiI+HO+CD11c+ cells in total F4/80+ (C) or CD11c+ cells (D) in the spleen and liver were then calculated. Two independent experiments were performed (total n = 4–6 mice per time point), and representative graphs are shown. Means ± SEM are shown.