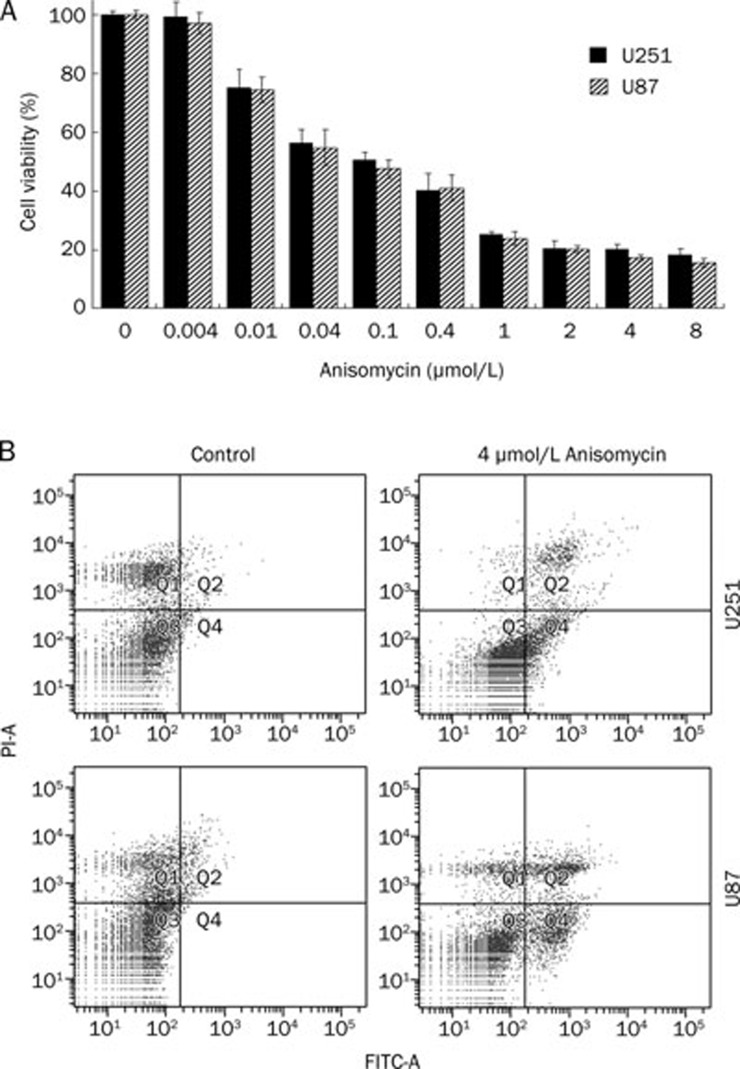
Figure 1.
Anisomycin inhibits U251 and U87 cell growth and induces cell apoptosis. (A) U251 and U87 cells were separately treated with anisomycin at concentrations of 0, 0.004, 0.01, 0.04, 0.1, 0.4, 1, 2, 4, or 8 μmol/L for 48 h. Cell viability was analyzed using CCK-8 kit. Anisomycin started to suppress U251 and U87 cell growth at concentration of 0.01 μmol/L (cell viability is 75.3%±6.1% for U251 and 74.4%±4.3% for U87). At 8 μmol/L, the cell viability is only 18.4%±2.1% for U251 and 15.6%±1.3% for U87. Anisomycin inhibits U251 and U87 cell growth in a concentration-dependent manner. (B) U251 or U87 cells were treated with 0 or 4 μmol/L anisomycin for 72 h, and double stained with annexin V-FITC conjugates and propidium iodide followed by analysing in a flow cytometer. The Q2 plus Q4 proportions indicated apoptosis cells, 4 μmol/L anisomycin caused 21.5%±2.2% of apoptosis proportion in U251 cells and 25.3%±3.1% in U87 cells.