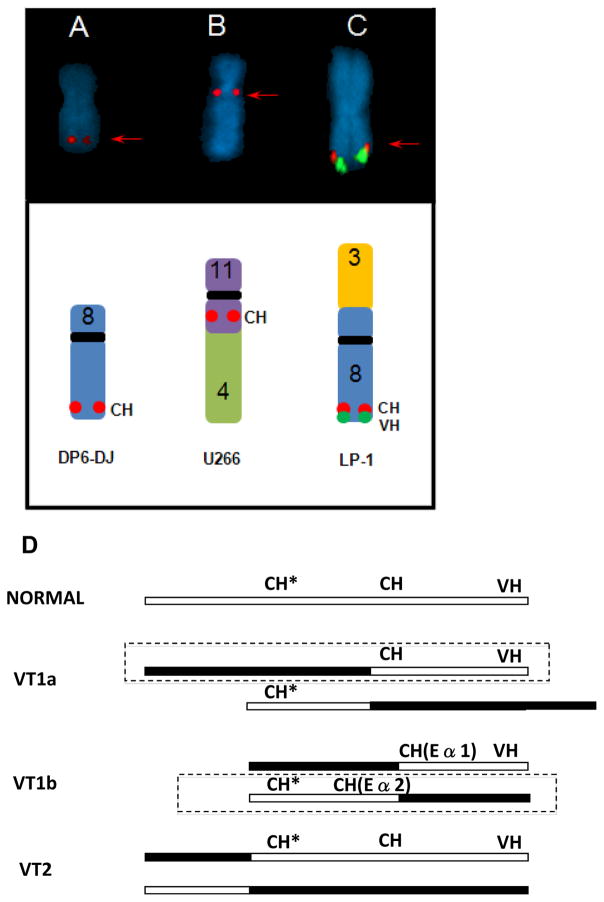
Figure 2.
Examples of complex IGH rearrangements. (A–C) Red arrows indicate signals that are detected by the Cytocell/in-house probes, but not detected with the Vysis probe. (A) der(8) with CH insertion. (B) der(11)t(4;11)(?;q14) with CH inserted at 11q13. (C) der(3)t(3;8) VT1a variant IGH translocation (CH and VH signals near chromosome arm 8q telomere) (D) anatomy of VT1a, VT1b, and VT2 variant IGH translocations where the open box depicts chromosome 14 and closed box another chromosome, CH includes Eα1 or Eα2 enhancer sequences detected by in-house or Cytocell probes, CH* represents sequences detected by 3′ Vysis Probe, and VH represents sequences detected by all 3 VH probes. The boxed derivative chromosome is expected to have a target gene dysregulated by Eα1 or Eα2. Note that the CH probe hybridizes to Eα1 and Eα2 sequences, consistent with the presence of CH signals on both derivative chromosomes in the VT1b variant IGH translocation.