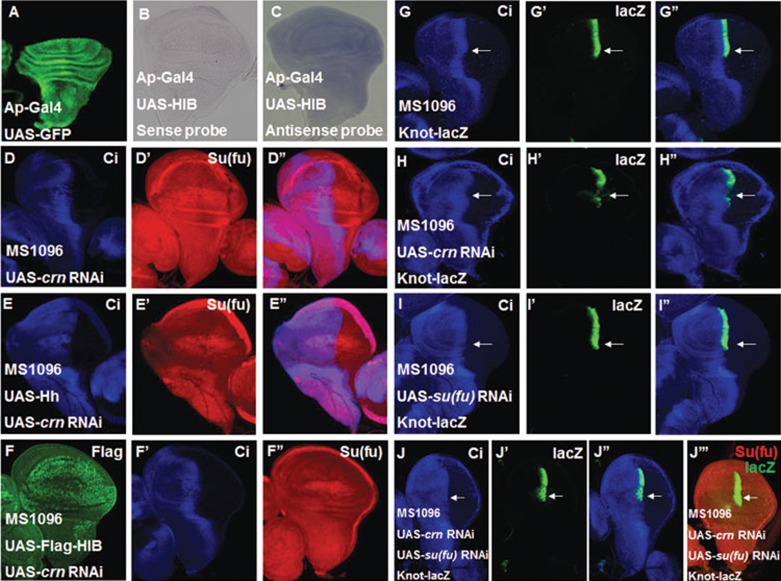
Figure 5.
HIB inhibits Su(fu) level through splicesome factor Crooked neck (Crn). (A) UAS-GFP (green) marked the Ap-Gal4-mediated gene expression pattern. AP-Gal4 drives UAS transgenes to be specifically expressed in the dorsal region of wing discs. (B, C) Overexpression of HIB with AP-Gal4 did not change su(fu) mRNA level in the dorsal region of wing discs as determined by in situ hybridization assay. Su(fu) sense probe was used as control (B), and Su(fu) antisense probe detected su(fu) mRNA level (C). (D-D'') Knockdown of crn with MS1096 upregulated Su(fu) protein level in the wing pouch region. (E-F'') Wing discs expressing UAS-crn-RNAi together with UAS-Hh (E-E'') or UAS-Flag-HIB (F-F'') were immunostained with CiFL (blue) and Su(fu) (red) antibodies. Simultaneous overexpression of UAS-Hh or UAS-Flag-HIB and UAS-crn-RNAi phenocopied crn knockdown. (G-J'') crn knockdown through MS1096 significantly reduced the expression of Knot-lacZ (indicated by arrows) near the A/P border (compare H' with G'), and co-overexpression of su(fu) RNAi prevented the reduction in Knot-lacZ expression (indicated by arrows) in wing discs (I-J''). (J''') Co-overexpression of su(fu) RNAi downregulated endogenous Su(fu) level (red) revealed by immunostaining with an anti-Su(fu) antibody. Of note, MS1096 exhibited higher expression in the dorsal region than in the ventral region of wing discs.