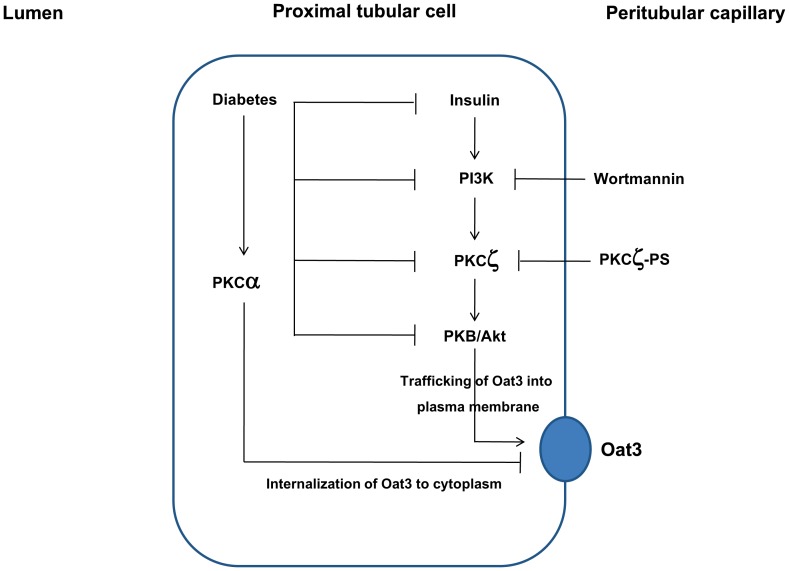
Figure 8. A hypothetical model for the regulation of renal Oat3 in diabetic condition.
Insulin regulates Oat3 function by activating PKCζ and PKB through PI3K leading to up-regulation of Oat3 function and increased trafficking of Oat3 to plasma membrane and subsequently increased transport function. The impairment of renal insulin signaling in diabetes down-regulates Oat3 function through PI3K/PKCζ/Akt/PKB-mediated pathway. The hyperglycemia-induced activation of PKCα in diabetes leads to internalization of Oat3 to cytoplasm resulting in down-regulation of Oat3 function. Alterations in the internalization and trafficking, the regulatory proteins, and the expression of Oat3 lead to decreased renal Oat3 function in diabetes. These changes can be recovered after insulin treatment for four weeks.