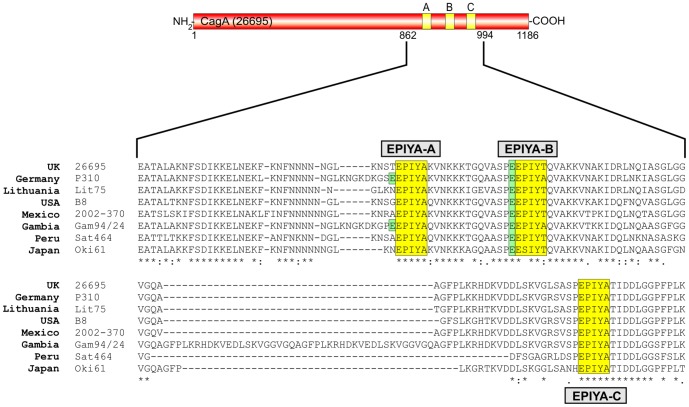
Figure 3. Sequence comparison of the EPIYA-motifs in CagA proteins from different clinical H. pylori strains used in the study.
Western CagA proteins of Helicobacter pylori vary in the carboxy-terminal phosphorylation sites EPIYA-A, EPIYA-B, and EPIYA-C depending on their geographical origin. These EPIYA-repeats serve as tyrosine phosphorylation sites of CagA and can be targeted by c-Abl and c-Src kinases [24], [30], . Multiple EPIYA-segments A, B and C are shaded with yellow and variations in the flanking regions were found among clinical H. pylori isolates from different continents as indicated. One striking feature of EPIYA-B (and in some strains in EPIYA-A) is the presence of a negatively charged glutamate residue in the -4 position (shaded with green), which is highly conserved in EPIYA-B among the different H. pylori strains and may affect the binding capabilities of phosphotyrosine antibodies as discussed in the text. The CagA protein sequences were obtained from databases (Table 2) and sequence alignment was done using the ClustalW2 program (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/).