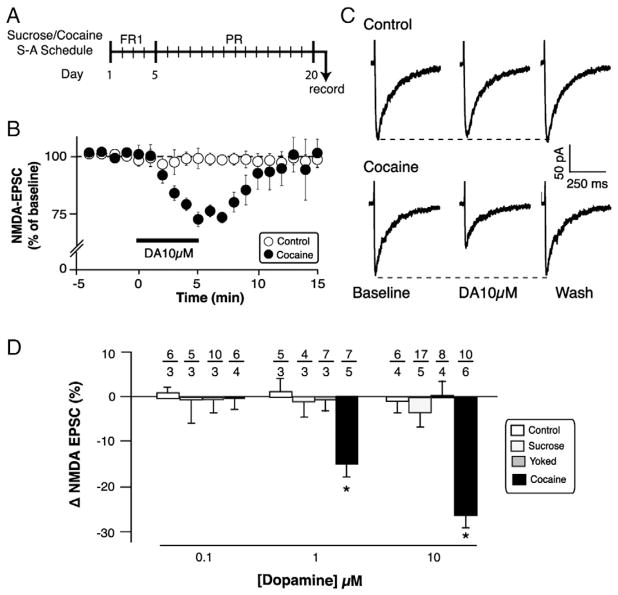
Fig. 1.
DA reduced whole-cell NMDA-EPSCs in ovBST neurons of cocaine self-administering rats. A. Schedule of sucrose and cocaine self-administration training. B. Effect of DA 10 μM on the amplitude of NMDA-EPSCs as a function of time in ovBST neurons. C. Representative NMDA-EPSCs in ovBST neurons of Control (top) and cocaine self-administering (bottom) rats without DA (left), after 5 min exogenous DA (middle), or after a 15-min wash (right). D. Summary of the effects of DA on NMDA-EPSCs in ovBST neurons. DA was significantly more potent at reducing NMDA-EPSCs in the cocaine self-administering group (group × dose interaction: F(6,79) = 4.6, p = 0.0005). *; significantly different from 0 (single sample mean t-tests). Number of neurons/rats indicated above each bar.