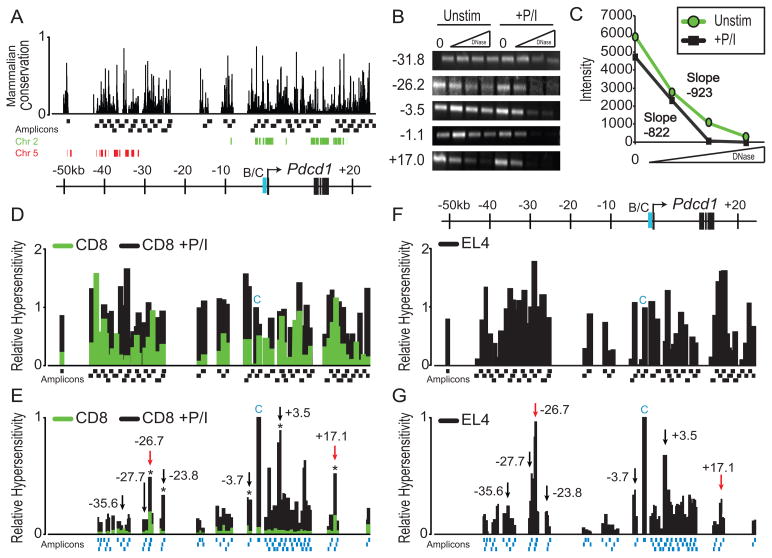
Figure 1. The Pdcd1 locus contains multiple inducible DNase I hypersensitive sites.
(A) Schematic of the PD-1 locus showing relative positions to the TSS, conservation of sequences among mammals defined by MULTIZ alignment, and the human chain alignment of chromosome 2 (green) and 5 (red) (58, 70). Amplicons (Black boxes) used for conventional PCR-based DNase I hypersensitivity analysis are shown as is the previously defined CR-B/C regulatory region (B/C, blue). Using increasing amounts of DNase I, each of the 59 amplicons were used to assess the DNase I hypersensitivity of splenic CD8 T cells (control or stimulated with PMA and ionomycin (+P/I) ex vivo for 24h). Each PCR amplicon is between 0.9–1.3 kb in length. (B) Select examples of the 59 amplicons that were evaluated by conventional PCR are shown and their position from the TSS is indicated. (C) Each of the 59 amplicons was quantitated using ImageJ software. The bands from the +17.0 PCR shown in B were used as an example with slopes determined by linear regression. (D) Relative DNase I hypersensitivity of CD8 T cells for unstimulated (green) and PMA/Io cultured cells (black). DNase I sensitivity was calculated by taking the negative value of the slope following ImageJ quantitation and normalizing to the previously known hypersensitive region CR-C. Amplicon locations are shown below. The amplicon representing CR-C is shown with a blue C. (E) A higher resolution DNase I hypersensitivity map was constructed using real-time PCR on PMA/Io stimulated CD8 T cells. Asterisks above bars indicate regions that were chosen for further analyses that showed a statistically significant (p <0.05) increase in DNase I hypersensitivity over control samples. Black and red arrows denote regions chosen for further study and the location of these regions with respect to the TSS is indicated. The DNase I sensitivity for each of the regions indicated by the arrows was statistically significant (p <0.05). Amplicons are displayed as blue boxes along the bottom. (F) Relative hypersensitivity of the Pdcd1 locus in the murine EL4 T cell line using the same methodology as in CD8 T cells from D. (G). Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of DNase I hypersensitivity in EL4 cells using the methodology from E. The data from these experiments were averaged from three independent cell preparations.