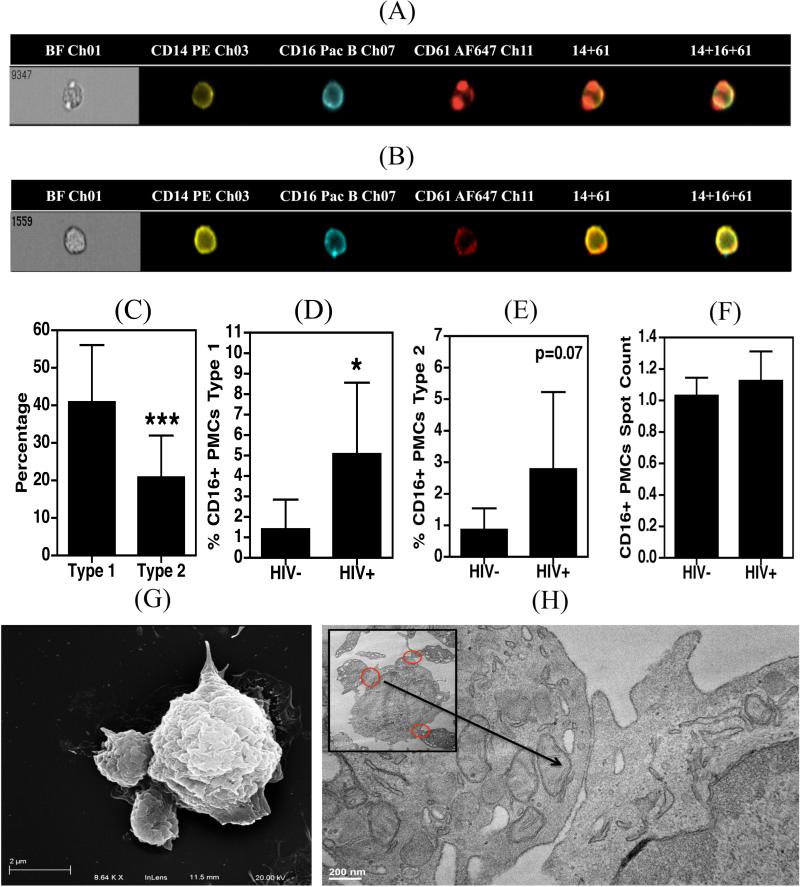
Figure 2. Morphological characterization of PMCs.
A-F. 100 μL whole blood obtained from HIV+ (n=5) and HIV− (n=6) donors was fixed, stained with antibodies against CD14, CD16 and CD61 and acquired on an Amnis Imagestream flow cytometer. A and B. Representative images of type 1 and type 2 CD16+ PMCs, respectively. C. Type 1 complexes were more prevalent in HIV infected and uninfected samples. D and E. HIV infected individuals contain significantly higher percentages of type-1, and -2 PMCs. F. The average number of platelets per monocyte in a PMC did not differ between the two study groups. G and H. Monocytes were isolated from PBMCs derived from HIV seronegative subjects (n=3) and were allowed to adhere to the culture dishes for 2 hrs. Cells were further processed for SEM (G) and TEM (H). In panels (A) – (F) samples were compared using an unpaired t-test which indicated significance as *p<0.05 and ***p<0.001.