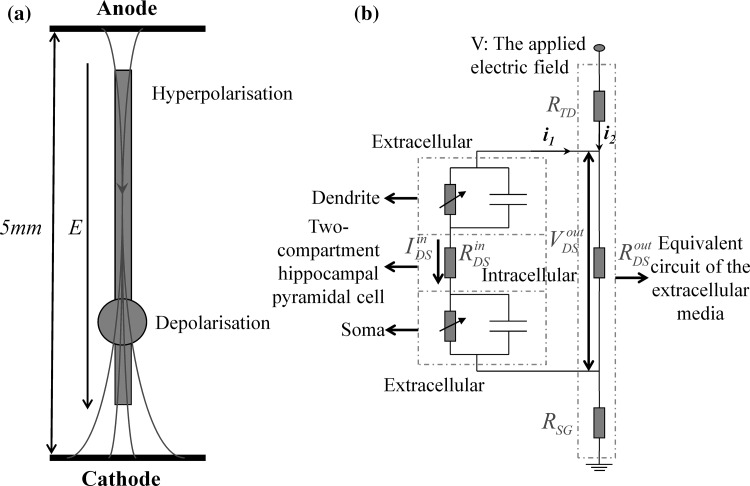
Fig. 1.
The two-compartment electric field effects model under the ephaptic transmission. a The schematic diagram of a single hippocampal pyramidal neuron in uniform electric field generated by two wire electrodes. An anode is located close to the apical dendrites and the cathode close to the soma and basilar dendrites. Current enters the apical dendrites, generating membrane hyperpolarization, and leaves the cell in the somatic and basilar region, generating membrane depolarization. With the conversion of cathode and anode, the current direction is reversed, generating hyperpolarization in the soma and depolarization in the apical dendrites respectively. b An equivalent model of the electric fields effect on a two-compartment single neuron embedded within a resistive array modeling the extracellular medium i.e. the ephaptic transmission. Here we define the three currents i 1, i 2 and I inDS with the reference positive direction shown in this figure, which are detailed described and used in “Appendix”