Fig. 1.
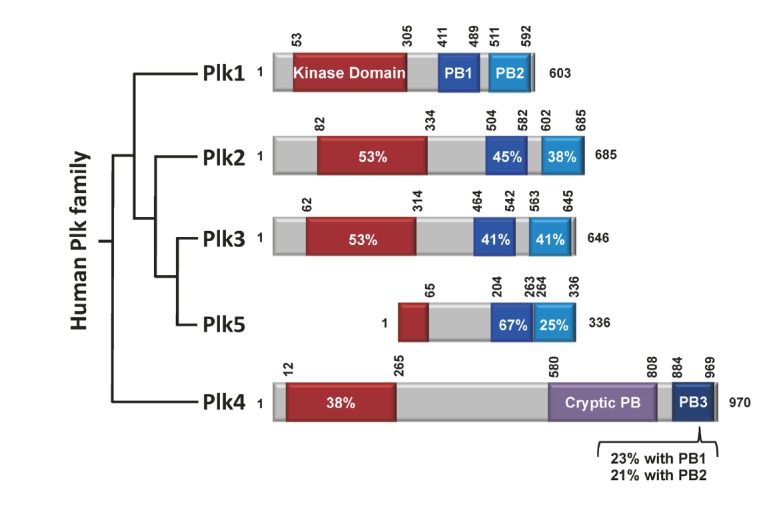
Schematic diagram of human Plk1 to Plk5. Plk1-4 contain the kinase domain (red) at their N-termini. The polo-box domains (PBDs) of Plk1-3 are composed of two structurally similar PB1 (blue) and PB2 (light blue) motifs that form a phospho-recognition module (Elia et al., 2003b). Whether the PBD of Plk5 also binds to a phospho-epitope is not known. In contrast to the PBDs of Plk1-3, the cryptic polo-box (CPB) of Plk4 homodimerizes to form a stable dimer (Leung et al., 2002; Slevin et al., 2012) and bind to a target in a manner that does not require a phosphorylated motif (Kim T.S. and K. S. Lee, unpublished data). In addition, PB3, which is thought to form a homodimer (Leung et al., 2002), exhibits a low level of homology with PB1 or PB2. Sequence identities with the corresponding domains in Plk1 are given in percentages. Numbers indicate the positions of amino acid residues in a given protein.
