Fig. 4.
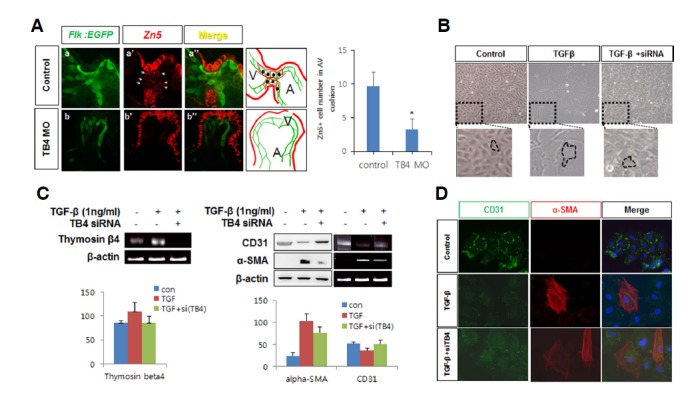
Thymosin β4 regulated EMT during zebrafish heart valve formation. (A) Endocardial cells expressing GFP in control Tg(flk: EGFP) embryos were immunostained with anti-Zn5 antibody at 48 hpf in control (arrowhead, a′) and zTB4 morphants (arrowhead, b′) and observed under a confocal microscope (X800). Green (endocardial cells) and red fluorescent (Zn5: EMT marker) cells are shown in the schematic diagram shown in right boxes (V; ventricle, A; atrium). Numbers of Zn5+ cells were counted and plotted (right panel) (n = 3). (B) Aortic valve endothelial cells were treated with TGFβ1 (1 ng/ml) for 8 days in EBM basal media in the presence or absence of TB4 siRNA. Cell morphologies were observed; results are shown in the upper pictures and in magnified images in the lower panels. (C) Semiquantitative RT-PCR for thymosin β4 and β-actin mRNA was performed using the same samples in (B) (left panel) (n = 3). Cell lysates obtained from the same samples were analyzed for the expressions of CD31 and α-SMA protein and mRNA by Western blotting (left) or semiquantitative RT-PCR (right) (right panel). β-Actin was used as an internal loading control. The quantitative expression of each gene are plotted (n = 3). (D) Aortic valve endothelial cells were grown for 8 days in the absence or presence of TGF-β or TB4 siRNA in EBM basal media. Cells were immunostained with anti-CD31 and anti-α-SMA antibodies. Green (CD31) and red fluorescent (α-SMA) cells were observed under a confocal microscope. Scale bar = 10 μm.
