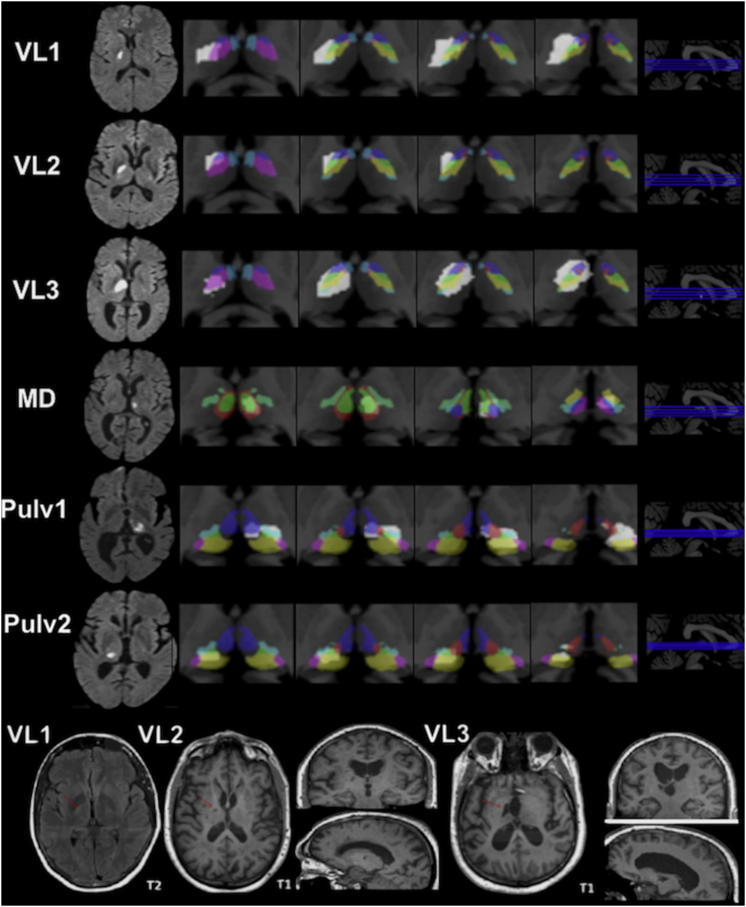
Figure 1.
Lesion Maps of Thalamic Patients
For the sake of simplicity, patients (n = 6) are labeled by the name of the thalamic lesion site showing overlap across them. Diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) scans (left column) illustrate the thalamic lesion site in the acute stage. Individual lesions were mapped onto a 3D, high-resolution, histology-based atlas of thalamic areas [18]. Axial slices to the right depict the thalamic nuclei in different colors, and the lesion area is highlighted in white. Table S1 depicts the percentage of damage of each thalamic nucleus and connectivity information from a diffusion tensor imaging atlas of probabilistic connections between thalamic nuclei and cortical regions [14]. The critical VL lesions included VLa, VApc, VLpv, and VLpd, which are densely connected with PFC [14]. The bottom row depicts high-resolution structural MRI of the VL patients acquired during the chronic stage following stroke. For patient VL1, we present the T2 brain scan rather than the T1 brain scan. Note that patient VL2 also had a small lesion in the left pallidum.
Details: VL patients’ lesions involved VLa (green), VLpv (yellow), VLpd (violet), VApc (blue), VPla (light cyan), and VAmc (red). Note that only the VL3 lesion involved part of the anterior nuclei (AD and AV; dark cyan). The lesions in our MD patient mainly involved MDpc (green), CL (red), CM (blue), Pf (violet), VM (yellow), VPM (cyan), and VPLp (light green). The pulvinar patients’ lesions involved PuA (green), PuL (violet), PuM (yellow), CM (red), MDpc (blue), and VPLp (cyan).
The following abbreviations are used: VAmc, ventral anterior magnocellular; VApc, ventral anterior parvocellular; VLa, VL anterior; VLpd, VL posterior dorsal; VLpv, VL posterior ventral; VPla, ventral posterolateral anterior; MDpc, mediodorsal parvocellular; Pf, parafascicular; CL, central lateral; CM, central medial; VM, ventral medial; VPM, ventral posteromedial; PuM, medial pulvinar; PuL, lateral pulvinar; PuA, anterior pulvinar.