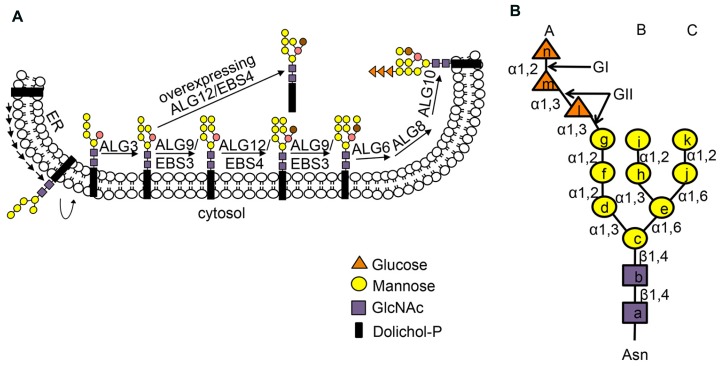
FIGURE 1.
(A) Stepwise assembly of N-glycan precursor on the ER membrane. The assembly of the N-glycan precursor starts at the cytosolic face of the ER membrane by adding two GlcNAc and five Man residues to the membrane-anchored Dol-PP linker. The resulting Dol-PP-Man5GlcNAc2 flips over into the ER lumen. Four Man residues are sequentially added to the flipped Dol-PP-Man5GlcNAc2 by three mannosyltransferases, ALG3, ALG9 (known as EBS3 in Arabidopsis) and ALG12 (known as EBS4 in Arabidopsis) with the ALG9 catalyzing two reactions of adding the terminal α1,2 Man residues on the middle and right branches. Three Glc residues are subsequently added to the right branch, generating the 14-sugar precursor, Dol-PP-Glc3Man9GlcNAc2. Two α1,6 Man residues are marked by brown and salmon color. The Dol-PP linker and different sugar residues are indicated. (B) The structure of N-linked Glc3Man9GlcNac2 glycan with three dimannose branches (branch A, B and C). Lower case letters inside sugar residues represent the order of sugar addition. The sugar linkage bonds and enzymes (GI, GII) that remove the three Glc residues are indicated. Figure adapted from Hong et al. (2009).