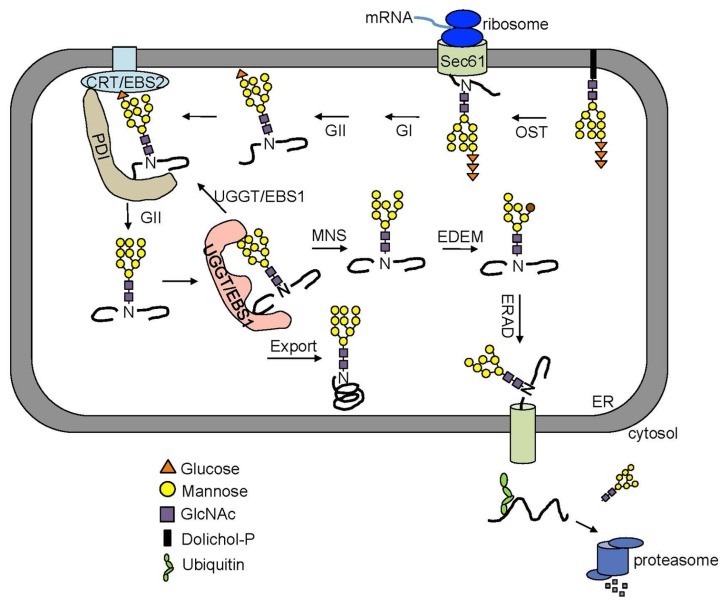
FIGURE 2.
An overview of the ERQC/ERAD system. Two Glc residues on the N-glycan of a nascent polypeptide are rapidly trimmed by GI and GII right after being transferred from the Dol-PP-linker. The resulting monoglucosylated N-glycans bind the two ER lectins CNX and CRT chaperone-assisted folding. The removal of this last Glc by GII releases a mature polypeptide from CNX/CRT. A correctly folded protein can leave the ER while an incompletely/mis-folded glycoprotein is recognized by UGGT (known as EBS1 in Arabidopsis) that adds back a Glc residue to the A branch, permitting its reassociation with CNX/CRT. A glycoprotein that fails to gain its native structure within a certain time window is removed from the folding cycle via sequential trimming of the two terminal α1,2 Man residues of the B and C branch by MNS1 (an ER-localized α1,2-Mannosidase, known as MNS3 in Arabidopsis) and Htm1/EDEM. A terminally misfolded glycoprotein with α1,6 Man-exposed glycan is selected to enter the ERAD pathway.