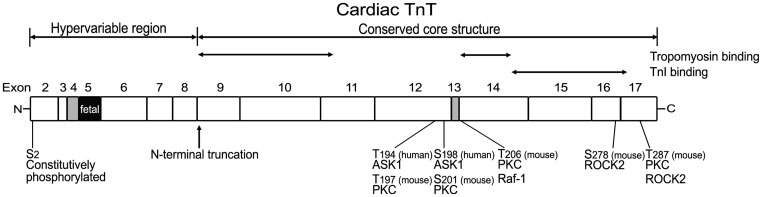
Figure 3.
Structural and functional domains of cardiac TnT, alternative spliced exons, and posttranslational modifications. Outlined on this linear map of cardiac TnT polypeptide (residue #s are those published in the original papers, which used various isoforms from different species), the functional segments T1, T2, and the N-terminal hypervariable region as well as the alternatively spliced exons 4, 5, and 13 are indicated. Ser2 is a highly conserved residue constitutively and phosphorylated in cardiac TnT in vivo (Perry, 1998; Sancho Solis et al., 2008). In vitro studies demonstrated that cardiac TnT could be phosphorylated by PKC at Thr197, Ser201, Thr206, and Thr287 in the C-terminal region that contains binding sites for TnI, TnC, and tropomyosin (Jideama et al., 1996). Thr206 can also be phosphorylated by Raf-1 (Pfleiderer et al., 2009) and Ser278 and Thr287 by ROCK2, which inhibited tension development and ATPase activity in skinned fibers (Vahebi et al., 2005). Thr194 and Ser198 of cardiac TnT have been found to be phosphorylated by ASK1 with decreases in cardiomyocyte contractility (He et al., 2003).