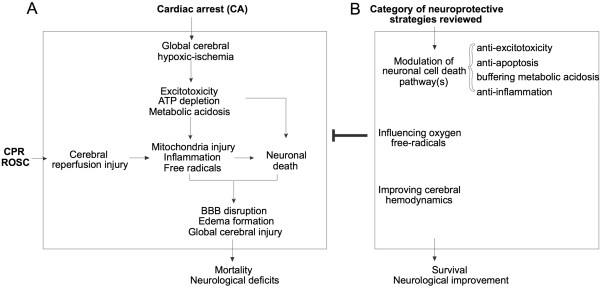
Figure 1.
Pathophysiology and possible mechanisms of protection following cardiac arrest. A: Comprehensive cascades of pathophysiology constituting global brain hypoxic ischemia and reperfusion injury following cardiac arrest (CA) and return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC). B: The possible mechanisms of protection investigated in literature included in this review were separated into three broad mechanistic categories. The effects of these interventions could decrease global brain injury after resuscitation from cardiac arrest and thus potentially improve survival and neurologic outcome.