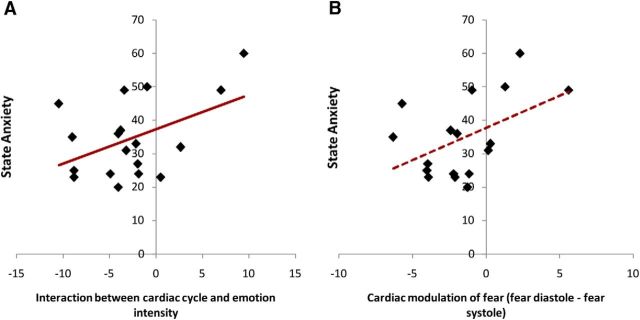
Figure 4.
The interaction between cardiac cycle and emotion correlated significantly with state anxiety (A). This was largely driven by cardiac modulation of fear (diastole − systole), which displayed a trend relationship with state anxiety (B). Therefore, the relative inhibition of threat processing at diastole was aberrant with anxiety, suggesting a potential mechanism contributing to sustained overreactivity to fear signal and threat in anxiety.