Figure 1.
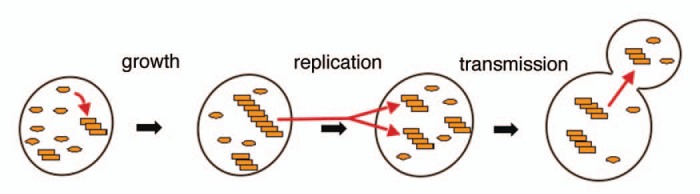
In order for prions to propagate stably in yeast they must grow, replicate and be transmitted efficiently to daughter cells (red arrows). Growth occurs when the soluble form of a prion protein (ovals) is converted into the prion conformation as it joins the end of a prion fiber (stack of rectangles). Replication occurs when prion fibers break into more numerous pieces that each can continue to propagate the prion conformation. Transmission of prions to daughter cells can occur by passive diffusion with cytoplasm.
