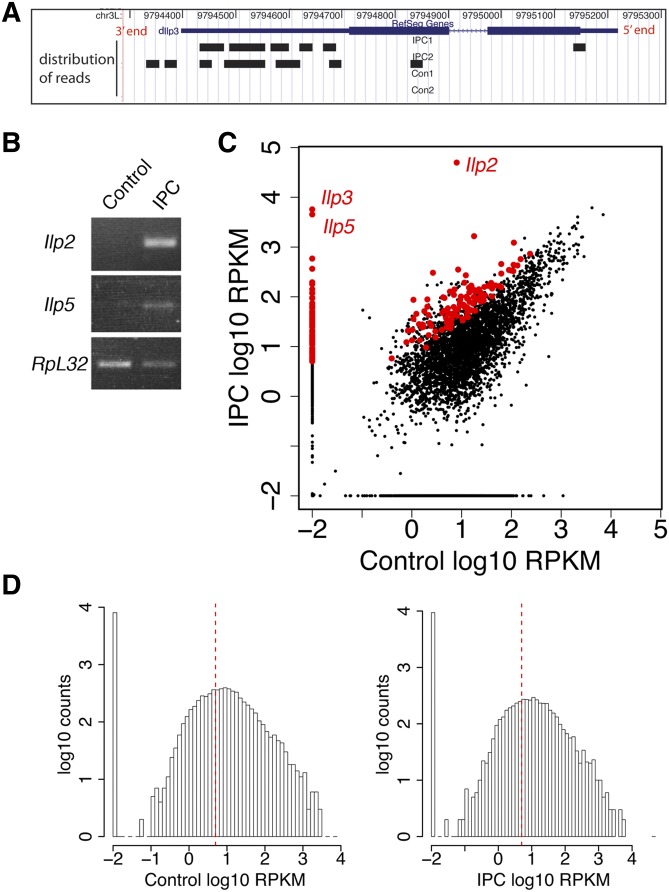
Figure 3.
mRNA sequencing of IPCs and control neurons. (A) A 3′ bias of mRNA sequencing reads. Distribution of mRNA-seq reads along Ilp3 mRNA as seen in the UCSC Genome Browser (Karolchik et al. 2003). RefSeq Gene track shows Ilp3 mRNA structure. Wide blue bar: exons; narrow blue bar: 5′ and 3′ untranslated region; blue line: intron. Distribution of mRNA reads from IPC1, IPC2, control 1, and control 2 samples is shown as black bars in individual tracks. (B) RT-PCR validation of laser-captured IPCs. Ilp2 and Ilp5 mRNA levels were assayed in amplified mRNAs from captured IPCs and control neural tissues. The housekeeping gene Ribosomal protein L32 (RpL32) was used as control. (C) Scatter plot of the mRNA-Seq expression data of IPCs and controls. Both the x- and the y-axis represent RPKM in log10 ratio. Red dots highlight IPC-enriched genes. A pseudo-count of 0.01 was added to RPKMs of all genes to avoid errors in log transformation of true. Thus, zero expression genes were represented as dots with expression of −2 in log10 on the plot. (D) Histograms of RPKM levels of genes expressed in controls and IPCs. The x-axis is log10 scale of gene expression measured in RPKM; the y-axis is gene counts in log10 scale. A pseudo-count of 0.01 was added to RPKMs of all genes to avoid errors in log transformation of true. The dashed red line represents RPKM = 5.