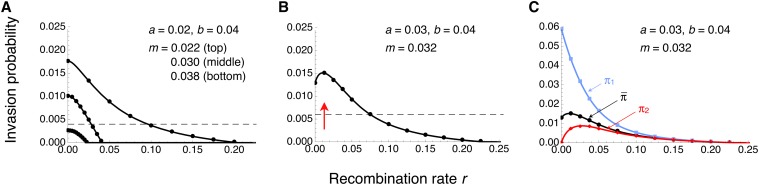
Figure 1.
Invasion probability of A1 as a function of the recombination rate for a monomorphic continent. (A and B) Weighted average invasion probabilitiy across the two genetic backgrounds B1 and B2 (Equations 2 and 4). For comparison, horizontal dashed lines give 10% of Haldane’s (1927) approximation 2a, valid for m = 0 and r = 0.5. (B) The optimal recombination rate ropt, defined as the recombination rate at which is maximized (red arrow), is nonzero. (C) Same as in B, but in addition to the weighted average, the invasion probabilities of A1 conditional on initial occurrence on the B1 or B2 background are shown in blue or red, respectively. Note the difference in the scale of the vertical axis between B and C. In A–C, curves show exact numerical solutions to the branching process. Dots represent the point estimates across 106 simulations under the branching-process assumptions (see Methods). Error bars span twice the standard error on each side of the point estimates, but are too short to be visible.