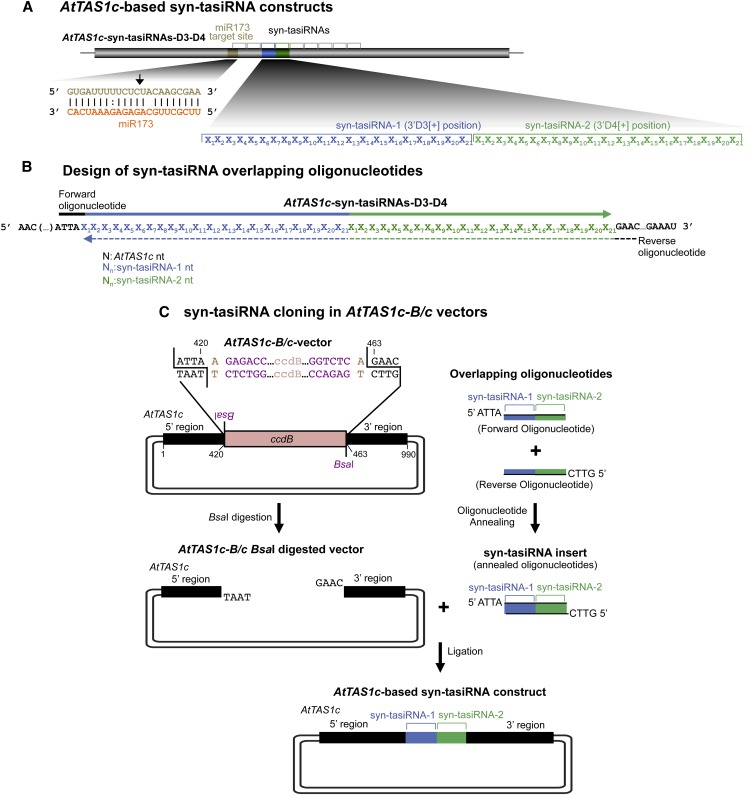
Figure 6.
Direct cloning of syn-tasiRNAs in vectors containing a modified version of AtTAS1c with a ccdB cassette flanked by two BsaI sites (B/c vectors). A, Diagram of AtTAS1c-based syn-tasiRNA constructs. tasiRNA production is initiated by miR173-guided cleavage of the AtTAS1c transcript. syn-tasiRNA-1 and syn-tasiRNA-2 are generated from positions 3′D3[+] and 3′D4[+] of the AtTAS1c transcript, respectively. Nt of AtTAS1c, miR173, syn-tasiRNA-1, and syn-tasiRNA-2 are in black, orange, blue, and green, respectively. B, Design of two overlapping oligonucleotides for syn-tasiRNA cloning. The sequences covered by the forward and reverse oligonucleotides are represented with solid and dotted lines, respectively. C, Diagram of the steps for syn-tasiRNA cloning in AtTAS1c-B/c vectors. The syn-tasiRNA insert obtained after annealing the two overlapping oligonucleotides has 5′-ATTA and 5′-GTTC overhangs and is directly inserted into the BsaI-linearized AtTAS1c-B/c vector. Nt of the BsaI sites and arbitrary nt used as spacers between the BsaI recognition site and the AtMIR390a sequence are in purple and light brown, respectively. Other details are as in A.