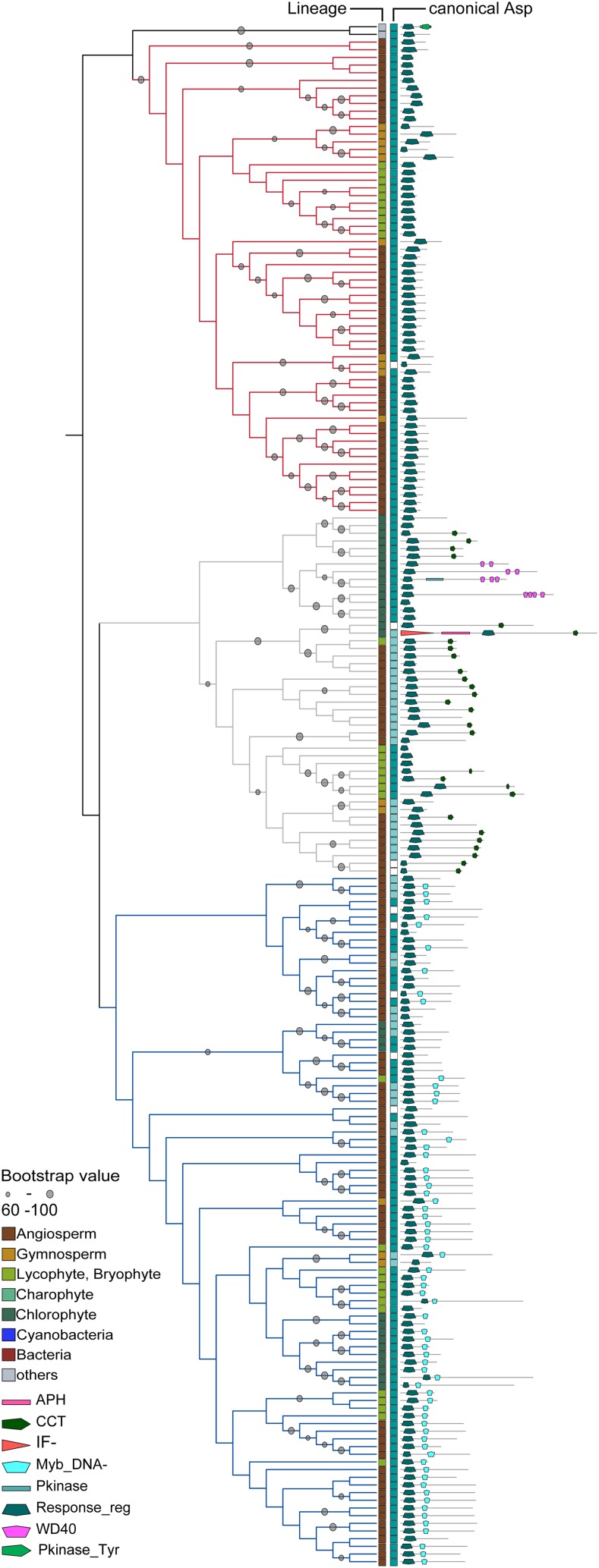
Figure 6.
Phylogenetic relationship of RRAs, RRBs, and PRRs. Left, Sequences of the RR domains were aligned, and an ML tree was calculated. Depicted is a subtree (protein identifiers are shown in Supplemental Fig. S5) from the global RR tree (Supplemental Fig. S1) containing the RRAs (red lines), RRBs (blue lines), and PRRs (gray lines). For canonical Asp, dark blue shows conservation of canonical Asp, light blue marks conservative substitution, and white boxes symbolize no conservation. Right, Domain architecture of the whole respective protein. Details are in “Materials and Methods.” Abbreviation of the domains are according to the Pfam-database (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk): Pkinase, PF00069; APH, PF01636; Response_reg, PF00027; CCT, PF06203; Myb_DNA-, PF00249; WD40, PF00400; and IF-, PF01008.