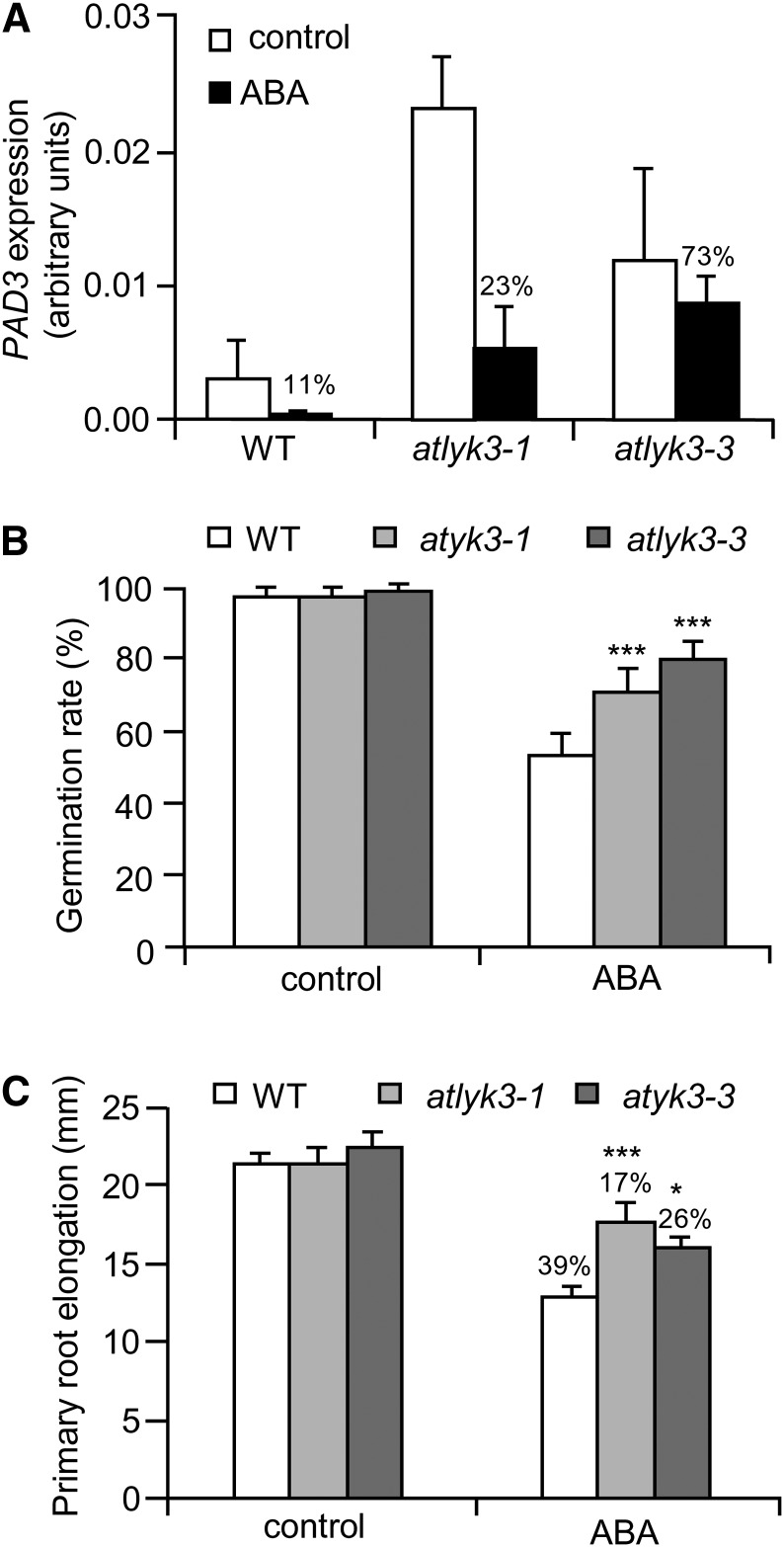
Figure 5.
AtLYK3 is required for full response to ABA. A, Wild-type (WT), atlyk3-1, and atlyk3-3 liquid-grown seedlings were treated for 24 h with 0.01% MeOH (control, white bars) or 10 μm ABA (black bars). Total RNA was extracted, and expression of PAD3 was analyzed by qPCR, using UBQ5 as reference. Bars indicate average expression ± sd of three independent biological replicates. For each genotype, the percentage of expression in ABA-treated samples, with respect to the control, is indicated above bars. B, Wild-type, atlyk3-1, and atlyk3-3 seeds were stratified for 3 d at 4°C and sown on solid medium supplemented with 0.05% MeOH (control) or 5 μm ABA. Germination rate was determined after 3 d. Bars indicate average percentage of germinated seeds in three independent experiments ± sd (n > 30 for each experiment). C, Wild-type, atlyk3-1, and atlyk3-3 seedlings were germinated on solid medium, and after 4 d, they were transferred to plates containing solid medium supplemented with 0.05% MeOH (control) or 2.5 μm ABA. Elongation of the primary root was measured after 2 d. Bars indicate the average elongation of roots from seedlings grown on ABA or on control plates ± sd (n > 10). The percentage of reduction of root elongation, with respect to the controls, is indicated above bars. Asterisks indicate significant differences between the wild type and mutants treated with the same conditions, according to Student’s t test (***P < 0.01).