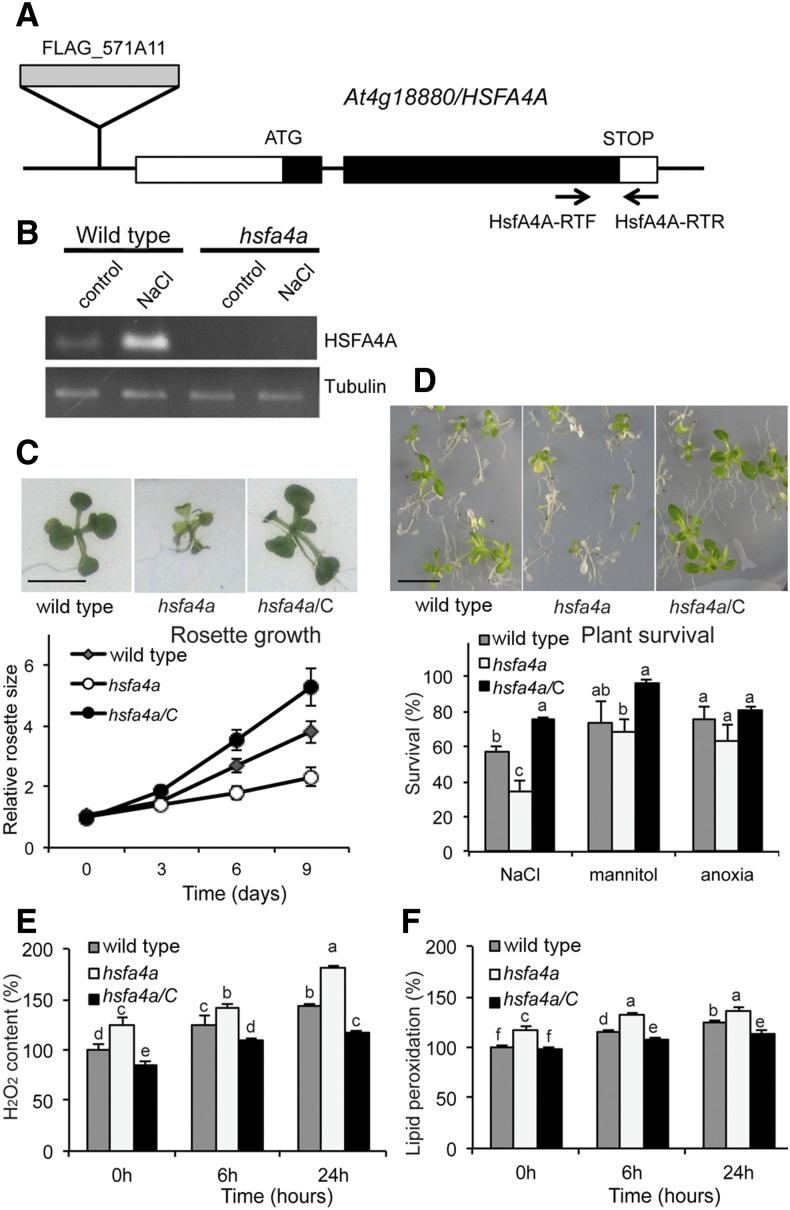
Figure 4.
The hsfa4a T-DNA insertion mutant is hypersensitive to salinity. A, Position of FLAG_57A11 T-DNA insertion in the At4g18880 gene and primers used for reverse transcription (RT)-PCR. B, RT-PCR analysis of HSFA4A transcription in wild-type and hsfa4a mutant seedlings treated with 100 mm NaCl for 6 h. C, Rosettes of the wild type, hsfa4a mutant, and complemented mutant (hsfa4a/C). Five-day-old seedlings were transferred to and grown on medium supplemented by 100 mm NaCl for 9 d. Graph shows relative rosette sizes on 100 mm NaCl, where 1 corresponds to size of wild-type seedlings on day 0. D, Survival of wild-type, hsfa4a mutant, and hsfa4a/C plants on high-salt medium (200 mm NaCl, 5 d). Viability of plants was scored 7 d after stress recovery. Graph shows survival rates after high-salt, osmotic (600 mm mannitol, 5 d), and anoxia treatments (8 h; see Fig. 2E). E and F, Accumulation of H2O2 (E) and lipid peroxidation rates (F) in plants subjected to salt stress (150 mm NaCl, 6 and 24 h); for these assays, whole seedlings were used. Bars = 1 cm. [See online article for color version of this figure.]