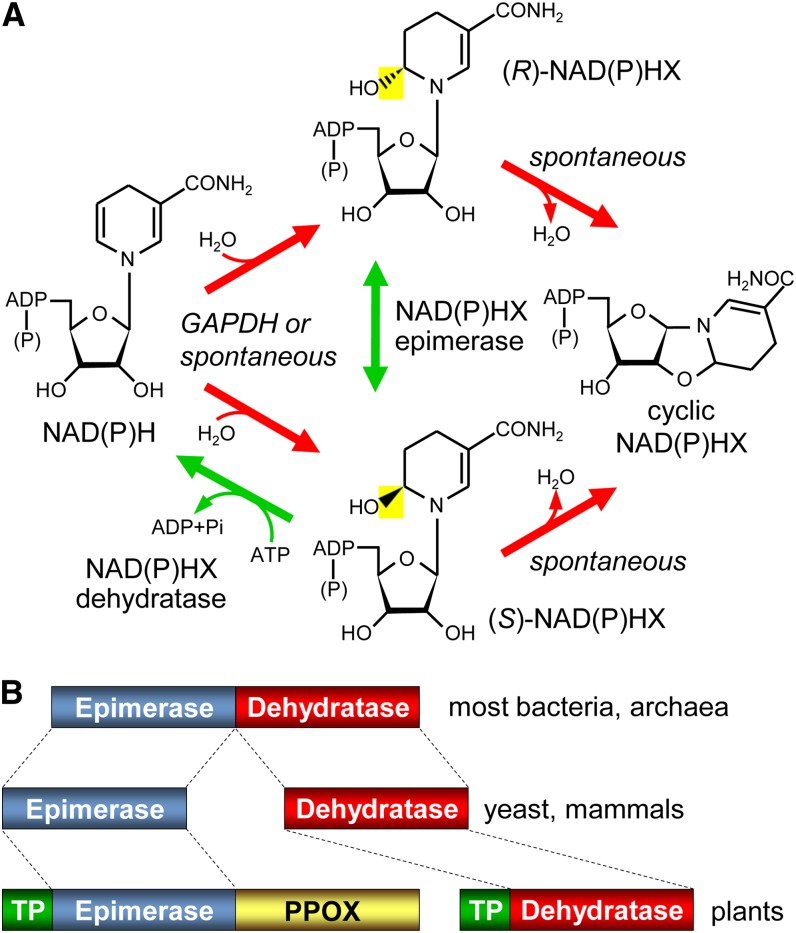
Figure 1.
NAD(P)H damage and repair reactions, and domain structures of the repair enzymes. A, The spontaneous or GAPDH-mediated hydration of NAD(P)H, and the enzymatic epimerization and dehydratase reactions that reconvert the resulting hydrates, (R)- and (S)-NAD(P)HX, to NAD(P)H. NAD(P)H hydrates can also spontaneously cyclize. The bacterial dehydratase reaction is ADP dependent rather than ATP dependent. B, Domain architectures of the NAD(P)HX epimerase and dehydratase enzymes of prokaryotes, yeast, and mammals, and of epimerase and dehydratase homologs in plants. TP, Predicted organellar targeting peptide.