Fig. 1.
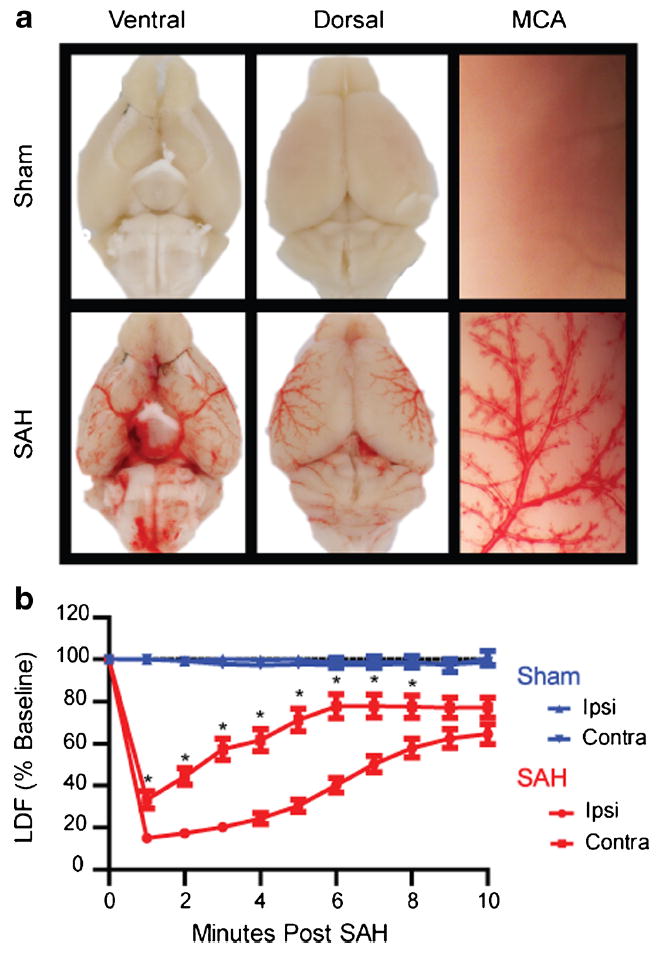
Validation of endovascular puncture model. a Mouse brains were perfused with heparinized saline to clear any intravascular blood and imaged 30 min after endovascular puncture. SAH mice show a wide distribution of extravasated blood throughout ventral (lower left) and dorsal (lower middle) brain surfaces. The magnified image of a perfused MCA (lower right) shows movement of extravasated blood along the paravascular pathway. b CBF measured by laser Doppler in both the ipsilateral (ipsi) and contralateral (contra) MCA territories of sham (blue) and SAH (red) mice. SAH mice (n=31) experience a rapid drop in CBF following puncture. Contralateral CBF recovers more rapidly than ipsilateral CBF, but both reach 65–75 % of baseline by 10 min (*p<0.05 contralateral different from ipsilateral)
