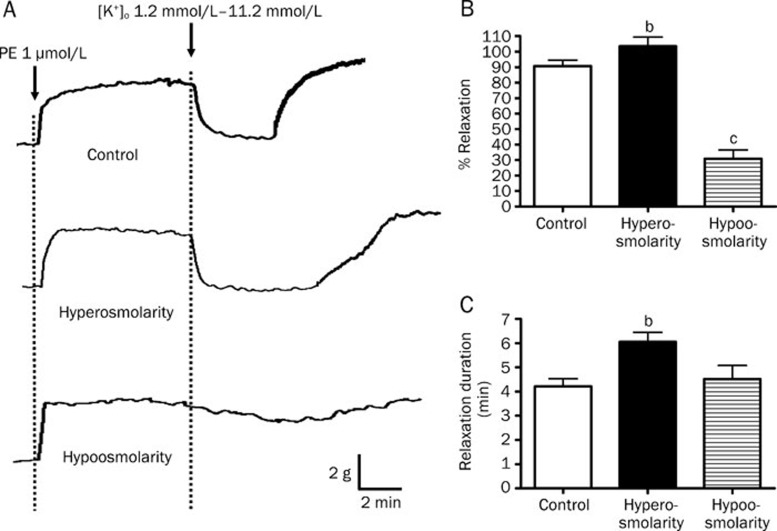
Figure 9.
Effects of hyperosmolarity and hypoosmolarity on K+-induced relaxation in rat mesenteric arteries. Arteries were incubated in normal bathing solution (300 mOsmol; control), hyperosmotic solution (300 mOsmol) or hypoosmotic solution (220 mOsmol) containing 1.2 mmol/L K+ in the presence of 100 μmol/L oubain. Arteries were then contracted by 1 μmol/L phenylephrine followed by changing the K+ level in bathing solution from 1.2 mmol/L to 11.2 mmol/L to induced relaxation. (A) Sample trace of K+-induced relaxation, (B) % relaxation of K+-induced relaxation and (C) duration of K+ -induced relaxation. Data were expressed as means±SEM (n=6). bP<0.05, cP<0.01 compared with control group.