Figure 13. Device that uses polyelectrolyte coatings and the shape of the paper for analyte separation and concentration.
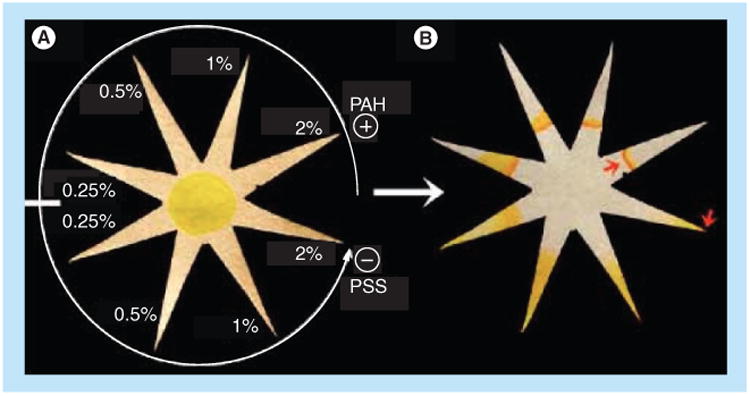
The surface charge in a given prong of the star, controlled via the concentration of polyelectrolyes as in the example in (A), affects the transport of model analyte fluorescein into that prong and can be tuned to produce highly concentrated fluorescein in a very small diameter tip, as shown by the rightmost arrow in (B).
PAH: Poly(allylamine hydrochloride); PSS: Poly(styrene sulfonate).
Reproduced with permission from [78] © American Chemical Society (2013).
