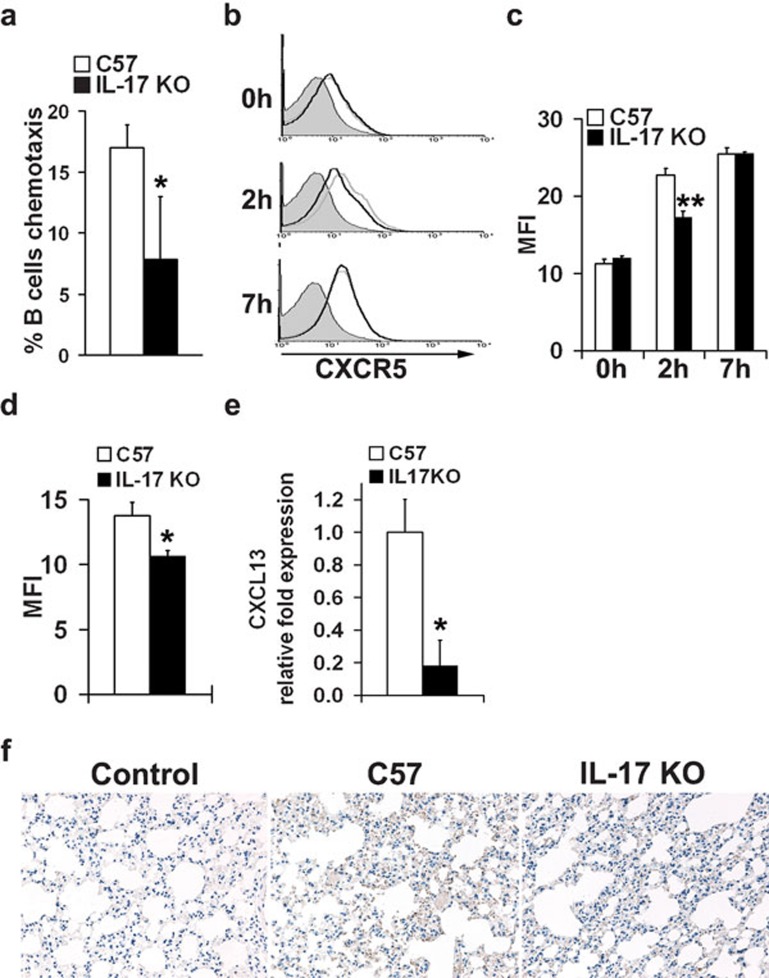
Figure 4.
Reduced B-cell migration to the lung in IL-17 KO mice. (a) Analysis of chemotactic migration of B cells towards CXCL13. Splenic B cells from both IL-17 KO mice and wild-type controls were purified with B220 microbeads and then subjected to a CXCL13 chemotaxis assay. Migrated cells were counted on a flow cytometer under a constant medium flow rate. Each treatment was performed with triplicate transwells. (b, c) CXCR5 expression in B cells from wild-type (gray lines) and IL-17 KO mice (black lines) upon stimulation of inactivated virus in vitro. Isolated splenic B cells were set up at 5×106 cells/ml in R10 with 10 µg/ml inactivated influenza virus VN1194. CXCR5 expression in B cells was evaluated before (0 h), 2 and 7 h after stimulation. Data were obtained in triplicate and expressed as MFI±s.d. detected by flow cytometry. (d) CXCR5 expression in B cells from the lungs of mice stimulated with inactivated virus in vivo. Both IL-17 KO mice and wild-type controls were stimulated i.n. with inactivated virus. Mice were killed at 48 h post-stimulation, and surface expression of CXCR5 in B cells from the lungs was analyzed by flow cytometry. Data were obtained from three animals in each group and expressed as MFI±s.d., as determined by flow cytometric analysis. (e, f) CXCL13 expression in the lung tissue of IL-17 KO mice and wild-type mice following H5N1 influenza virus infection. Mice were infected with H5N1 influenza virus and mRNA or protein levels of CXCL13 in lung tissue collected 5 dpi were evaluated by real-time PCR (e) and immunohistochemical staining (f), respectively (n=4 in each group). *P<0.01, **P<0.05. dpi, days post-infection; IL, interleukin; i.n., intranasally; KO, knockout; MFI, mean fluorescence intensity.