Figure 1.
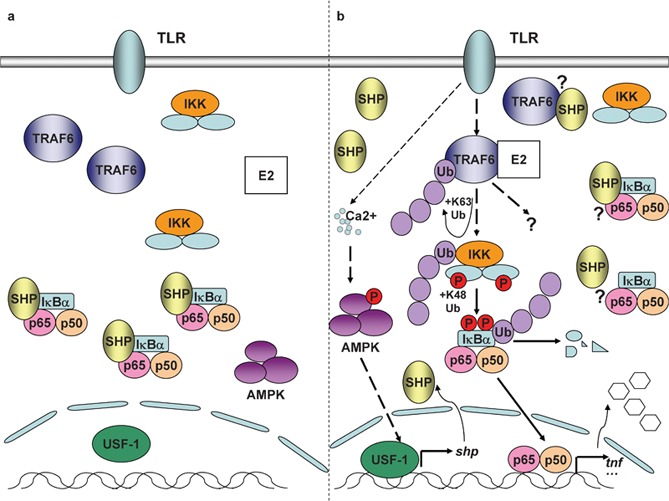
SHP in control of TLR signaling. (a) In unstimulated resting BMDMs, SHP interacts with p65, the major transactivating subunit of NF-κB. (b) TLR signaling induces dissociation of SHP from p65. TLR signaling simultaneously induces the expression of SHP in macrophages through Ca2+-dependent activation of AMPK. SHP in turn decreases TLR-triggered expression of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α by physically binding to TRAF6 and dampening TRAF6 ubiquitination. AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; BMDM, bone marrow-derived macrophage; IKK, IκB kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; SHP, small heterodimer partner; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor-necrosis factor-α TRAF6, TNF receptor-associated factor 6; USF-1, upstream stimulatory factor-1.
