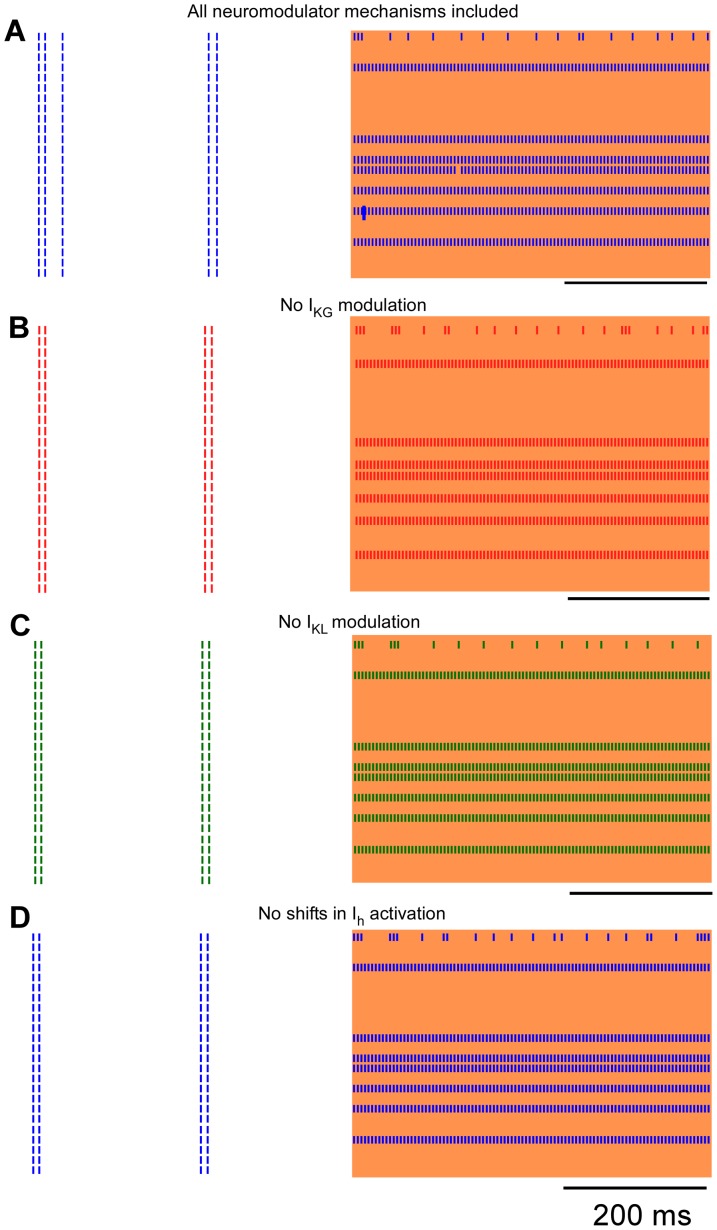
Figure 9. Impact of neuromodulator-dependent currents on responses of model thalamic neurons during stimulation.
Rasters of multiple model neurons in response to stimulation at 200 Figure 7 , but the timeline is expanded to show the responses of model neurons during simulation. a. Simulations were conducted with all of the neuromodulator-dependent mechanisms intact, and subsequently with each of the mechanisms removed individually from each simulation: b. neuromodulator-dependent activation of the pertussis toxin sensitive potassium current (IKG); c. Neuromodulator-dependent inhibition of a non-pertussis toxin sensitive leak potassium current (IKL); and d. Neuromodulator-dependent shifting of the activation curve of the hyperpolarization-activated cation current (Ih). The shaded region indicates the time when stimulation was on.