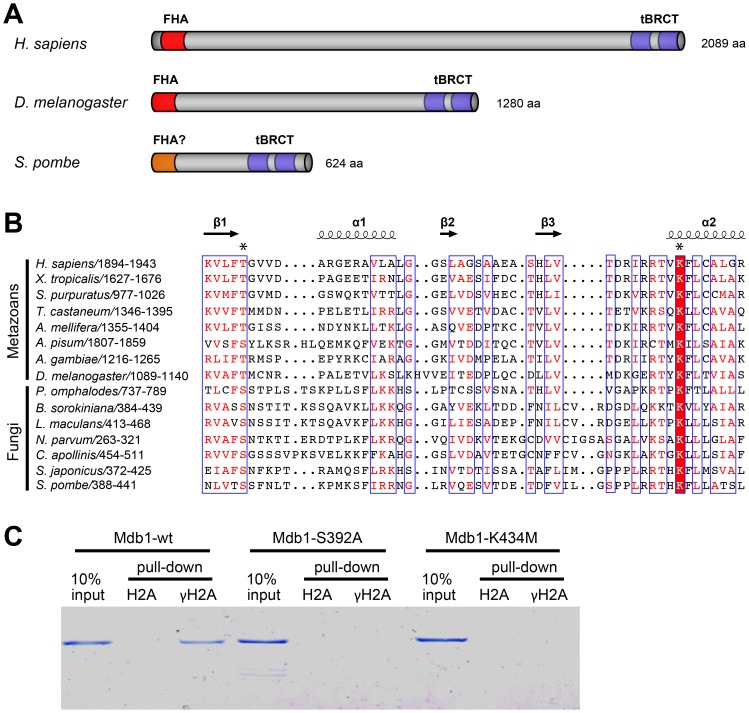
Figure 1. Mdb1 is a MDC1 homolog and binds γH2A directly.
(A) A schematic showing the domain organizations of human MDC1 (accession NP_055456), Drosophila ortholog of human MDC1 (accession NP_523887) [44], and S. pombe Mdb1 (accession NP_593964). The FHA domains and tBRCT domains are highlighted in red and blue, respectively. The N-terminal region of Mdb1 (amino acids 1–89) is conserved in the fission yeast species and is predicted to be rich in beta strands by secondary structure predictions. We speculate that this region may adopt a FHA-like fold, despite lacking obvious sequence homology to any known FHA domains. (B) A multiple sequence alignment of the N-terminal portion of the tBRCT domain in metazoan proteins related to MDC1 and fungal proteins related to Mdb1. The alignment was generated by MAFFT-L-INS-i [45]. Secondary structural elements of human MDC1 (PDB 2ADO) were visualized together with the alignment using ESPript [46]. The two residues directly involved in γH2AX binding in human MDC1 (T1898 and K1936) are labeled with asterisks. For the alignment of the whole tBRCT domain and the accession numbers of the sequences, see Figure S1. (C) Mdb1 directly binds a γH2A peptide in a manner dependent on the conserved phospho-binding residues in the tBRCT domain. Wild-type and two mutant versions (S392A and K434M) of Mdb1 proteins were expressed in bacteria and purified using the His6 tag. Biotinylated peptides that correspond to the C terminus of H2A.1, either unmodified (H2A) or phosphorylated on Ser-129 (γH2A), were incubated with the recombinant Mdb1 proteins. Peptides and associated proteins were pulled down by streptavidin Dynabeads and eluted by boiling in SDS-PAGE loading buffer. The eluates and 10% inputs were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie staining.