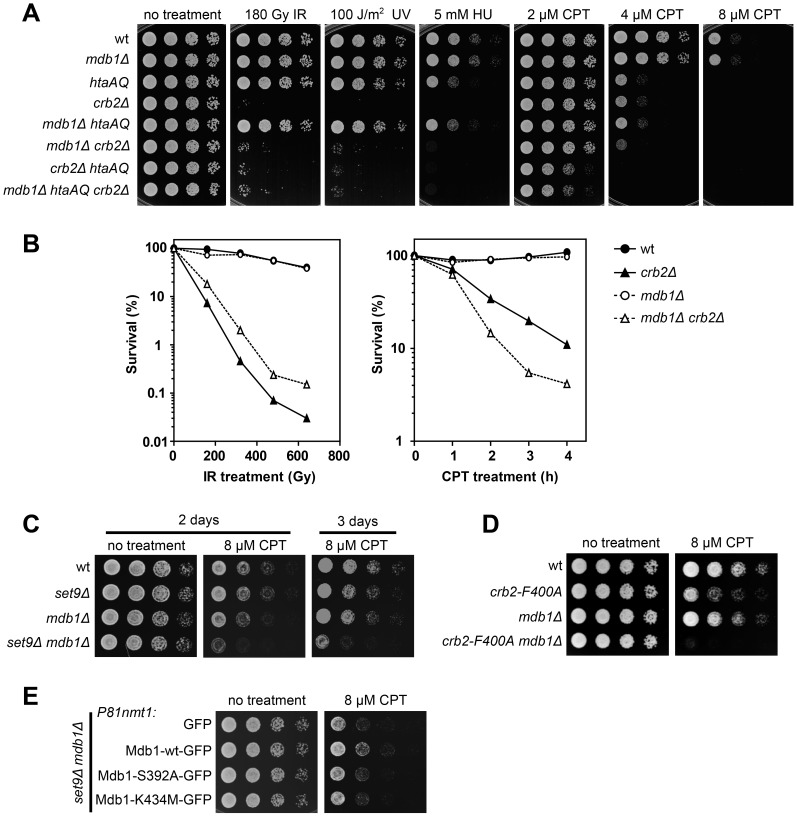
Figure 3. Loss of Mdb1 alters genotoxin sensitivity of crb2 and set9 mutants.
(A) mdb1Δ alters the genotoxin sensitivity of crb2Δ in a manner similar to htaAQ. Strains used were LD327, LD1067, LD574, LD197, LD1068, LD1070, LD678, and LD1071. (B) Quantitative survival curve analysis showed that mdb1Δ crb2Δ double mutant is less sensitive to IR, but more sensitive to CPT than crb2Δ single mutant. For the CPT treatment, cells were exposed to 20 µM of CPT for the duration indicated. Strains used were LD327, LD1067, LD197, and LD1070. (C) mdb1Δ set9Δ double mutant is more sensitive to CPT than each single mutant. Strains used were LD259, LD723, LD964, and DY15611. (D) mdb1Δ enhances the CPT sensitivity of a Tudor domain mutation in crb2, crb2F400A. Strains used were LD260, LD744, LD1011, and DY16269. (E) The phospho-binding residues are required for rescuing the CPT sensitivity of mdb1Δ set9Δ double mutant. GFP, Mdb1-wt-GFP, Mdb1-S392A-GFP, and Mdb1-K434M-GFP were expressed under the control of the P81nmt1 promoter. Cells were pregrown in a thiamine-free medium for 20 h before being spotted on CPT-containing thiamine-free plates. Strains used were DY15612, DY15607, DY15613, and DY15614.