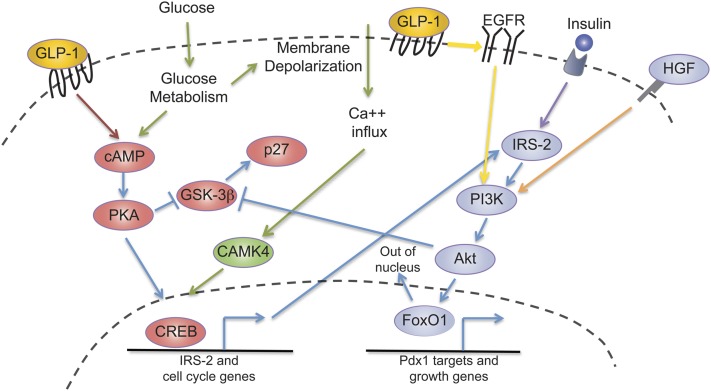
FIGURE 3.
Multiple pathways can stimulate β-cell replication in obesity, and there is overlap of many of the downstream activators. GLP-1 signals through the GLPR (red arrow) and leads to increased intracellular cAMP, which activates PKA. PKA then phosphorylates and activates the transcription factor CREB. Glucose metabolism (green arrows) increases cAMP levels and can activate the same pathway. PKA also inhibits GSK3-β, which is an activator of the cell cycle inhibitor p27. Glucose metabolism (green arrows) results in production of ATP and membrane depolarization, which leads to an influx of calcium ions. These calcium ions activate CAMK4, which then also phosphorylates and activates CREB. CREB stimulates transcription of IRS-2, which then provides IRS-2 protein necessary for insulin signaling. Insulin signals through the insulin receptor to phosphorylate and activate IRS-2 (purple arrow), leading to activation of PI3K and Akt. Akt inhibits GSK3-β. Akt is also necessary to phosphorylate the inhibitory transcription factor FoxO1 and promote its exclusion from the nucleus. When FoxO1 inhibition is released, transcription of Pdx1 and other genes promoting cell growth can be expressed. GLP-1 signaling can also transactivate EGFR (yellow arrow) and lead to activation of PI3K, ultimately signaling through the same pathways. HGF signaling through its receptor c-Met also stimulates PI3K (orange arrow). Therefore, there is great overlap in the downstream pathways that are involved in signaling in response to GLP-1, glucose metabolism, insulin, and HGF. The cAMP/PKA, GSK3-β, CREB, and IRS-2/PI3K/Akt/FoxO1 pathways are used by multiple upstream mitogenic signals (blue arrows). This overlap suggests that perhaps multiple activators must be present to trigger β-cell proliferation physiologically, but additionally highlights the challenges of interpreting the importance of 1 upstream factor when a downstream target is manipulated experimentally. CAMK4, calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase; CREB, cAMP response element binding protein; EGFR, epithelial growth factor receptor; FoxO1, forkhead box O1; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; GLPR, glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; GSK3-β, glycogen synthase kinase 3-β HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; IRS-2, insulin receptor substrate 2; Pdx1, pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1; PI3K, phosphoinositide-3 kinase; PKA, protein kinase A.