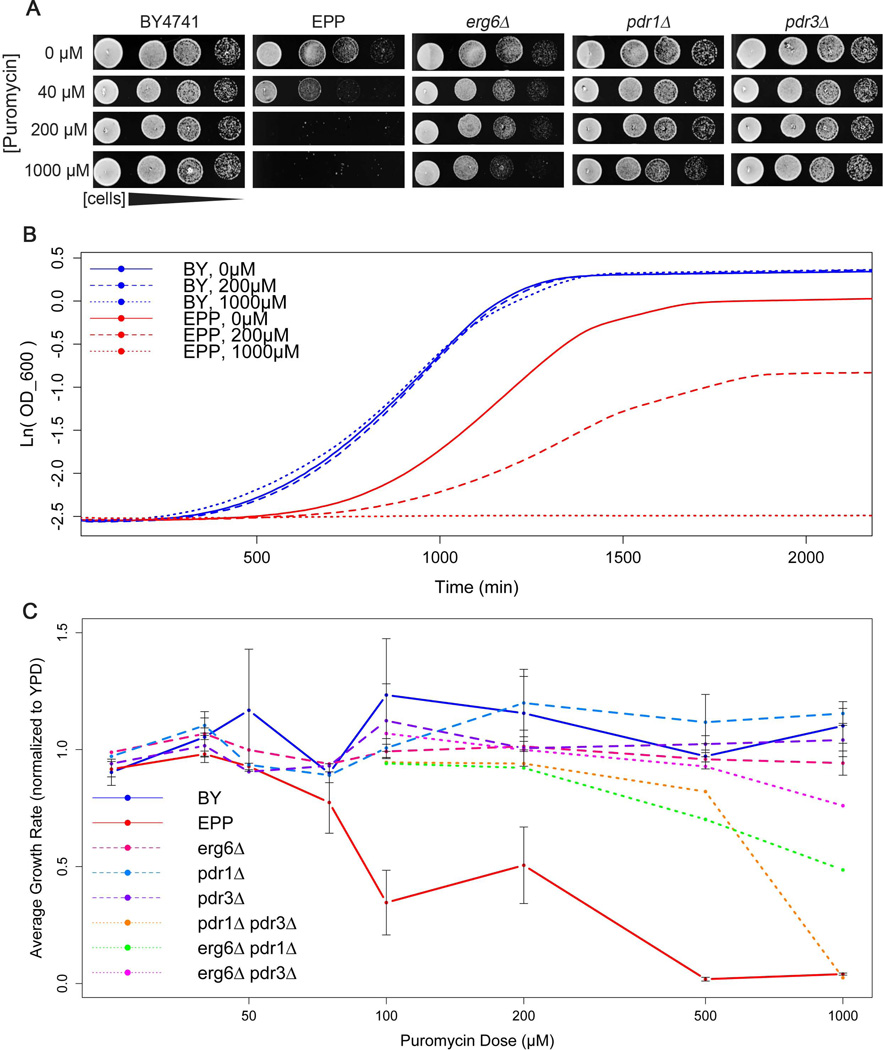
Figure 1.
Characterization of a puromycin-sensitive yeast strain. (A) Growth of 5-fold serial dilutions of wild-type (BY4741), EPP (erg6Δ pdr1Δ pdr3Δ) triple deletion mutant, and single deletion mutants cells spotted on YPD agar containing 0 μM, 40 μM, 200 μM and 1000μM puromycin. (B) Growth curves for BY4741 (blue) and the EPP triple mutant (red) in liquid media containing 0 μM (solid), 200 μM (dash), and 1000 μM (dot) puromycin. Curves are the average of 6 biological replicates. Growth curves were measure using a Tecan Sunrise plate reader sampling OD600 at 15 min intervals at a constant temperature of 30°C. (C) Average maximum growth rate (maximum change in log(OD)/minute) calculated for each strain grown at each concentration of puromycin, normalized to average maximum growth rate for each strain in YPD without puromycin. Error bars +/− SEM. Wild type (blue, solid line), EPP (red, solid line), erg6Δ (magenta, dash line), pdr1Δ (light blue, dash line), pdr3Δ (purple, dash line), pdr1Δ pdr3Δ (orange, dotted line), erg6Δ pdr1Δ (green, dotted line), and erg6Δ pdr3Δ (pink, dotted line).