Figure 5. Approach to the Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis.
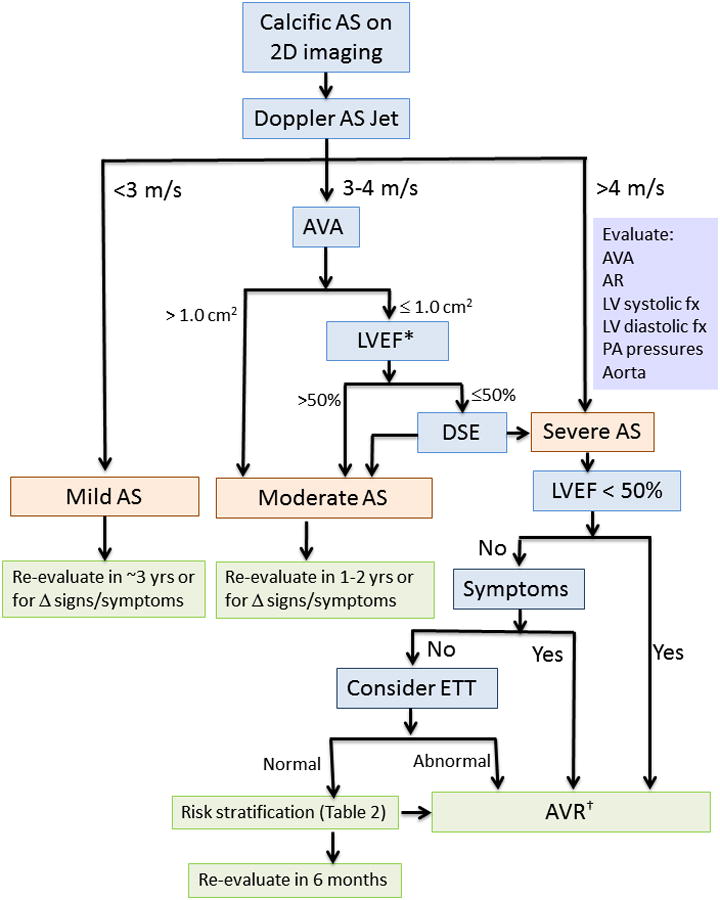
2D, two-dimensional; AS, aortic stenosis; AVA, aortic valve area; AR, aortic regurgitation; AVR, aortic valve replacement; DSE, dobutamine stress echocardiography; ETT, exercise treadmill testing; LV, left ventricular; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; PA pulmonary artery.
* A subset of patients presents with low flow, low gradient severe AS with preserved EF, characterized by a stroke volume index <35 ml/m2 and usually accompanied by LVH, a very calcified valve, small LV chamber, and reduced longitudinal systolic strain. See text for details.
† Surgical AVR is appropriate in most patients. Transcatheter AVR is recommended in inoperable patients and may be reasonable in patients with high surgical risk.
