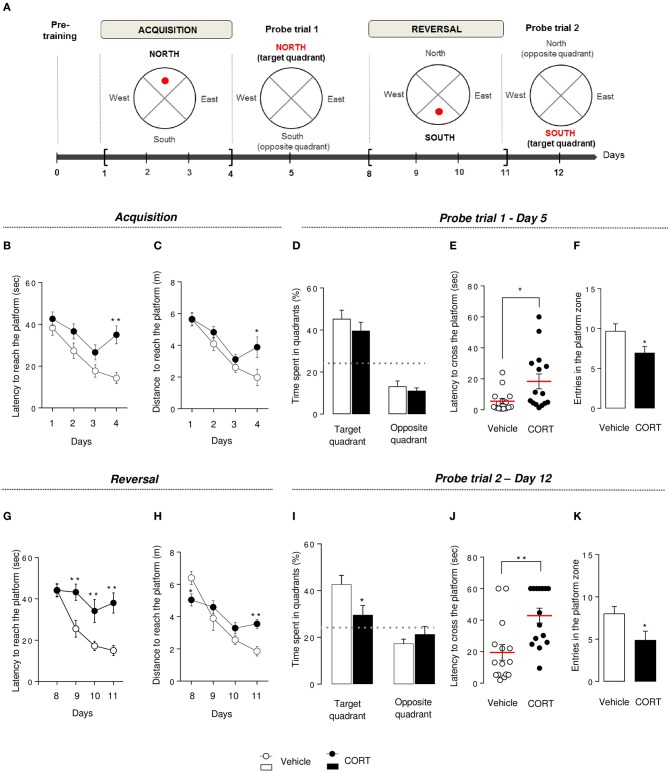
Figure 4.
Chronic corticosterone affects spatial learning performances, short-term memory and cognitive flexibility in the Morris water maze. Schematic diagram of the MWM experimental time course (A). After a pre-training phase (day 0), the MWM protocol was divided into 2 phases. Each phase includes a 4-day learning period followed by a probe session without the platform. During acquisition, mice learned to locate the platform in the target quadrant (North) then have to locate the platform in the opposite quadrant (South) during reversal. During acquisition, learning was expressed as the latency (B) and the total distance traveled (C) to reach the hidden platform during training sessions (Day 1–4). Short-term memory was assessed during the probe test in Day 5 by measuring the time spent into the target and the opposite quadrants (D), the latency to first cross the platform zone (E) and the number of entries in the platform zone (F). During reversal, learning, and cognitive flexibility were expressed as the latency (G) and the total distance traveled (H) to reach the hidden platform during training sessions (Day 8–11). Cognitive flexibility was assessed during the probe trial in Day 12 by measuring the time spent into the target and the opposite quadrants (I), the latency to first cross the platform zone (J) and the number of entries in the platform zone (K). Values are mean ± s.e.m., n = 10–15 animals per group; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 vs. vehicle group. The dotted-line indicates the chance level.