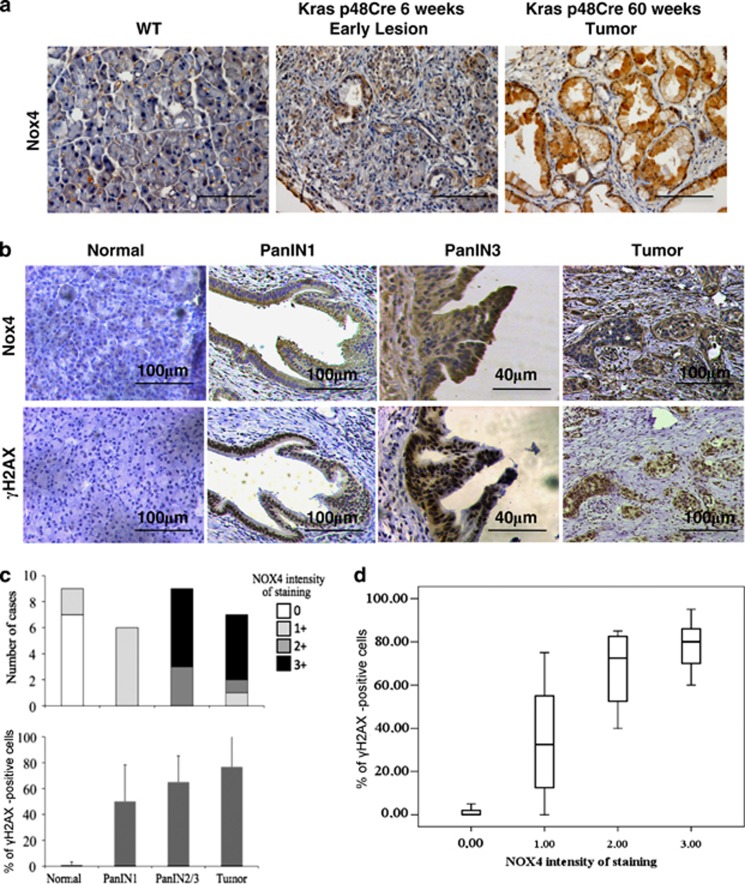
Figure 6.
Increased NOX4 expression is associated with pancreatic cancer progression and correlates with DDR accumulation. (a) Immunohistochemical staining of NOX4 on sections of WT and p48-Cre; LSL-KrasG12D mouse pancreata. In normal WT pancreas, Nox4 is not detectable in acinal or ductal cells, the proposed cells of origin of PDAC. In p48-Cre, LSL-KrasG12D animals, NOX4 becomes detectably expressed already in early PanINs and more robustly in late invasive lesions. Scale bar: 60 μm. (See also Supplementary Figure S6B). (b) NOX4 expression is undetectable by IHC in human normal pancreas, whereas its expression is upregulated in early panIN and late invasive tumors (upper panels). γH2AX immunohistochemistry on consecutive sections shows a staining pattern overlapping with that of NOX4. Scale bars are indicated. (c) Quantification of the staining in b. Two independent pathologists scored the intensity of cytoplasmic NOX4 staining and the percentages of γH2AX-positive nuclei in ducts, panINs and tumors. A scale from 0 (no staining) to 3+ (intense staining) was used. More than 50% of panIN3 and invasive lesions are strongly positive for NOX4. (d) NOX4 and γH2AX stainings correlate across the full spectrum of pancreatic lesions, from panINs to invasive