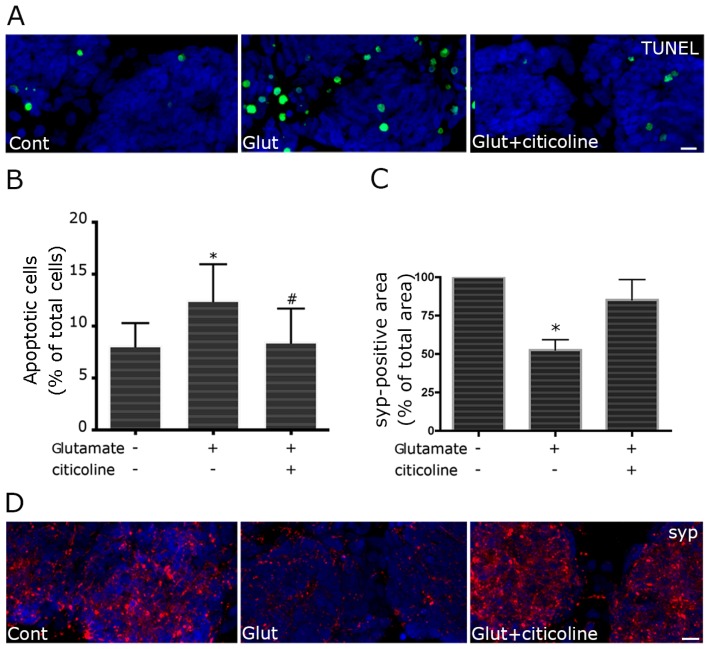
Figure 2.
Citicoline treatment protects retinal cells against glutamate-induced apoptosis and synaptotoxicity. To evaluate protective ability of citicoline against excitotoxicity, primary retinal cultures were treated with 100 μM citicoline 24 h before excitotoxic insult, induced with exposition to 100 μM glutamate for 25 min. The medium was then replaced with fresh Minimum Essential Medium/10% Fetal Calf Serum (MEM/FCS) and the cells were fixed after 24 h. Apoptosis was evaluated by TUNEL assay (A,B); Synapses were evidenced by immunolabeling of synaptophysin (C,D). In glutamate-treated retinal cultures, the increase in apoptotic nuclei (green) is counteracted by citicoline treatment (A); TUNEL-positive nuclei were counted and apoptosis was expressed as percentage of apoptotic cells over total cells. Bars represent the mean ± SEM of at least five independent experiments (B); Citicoline treatment significantly reduces the apoptotic rate in glutamate-treated cells. * p < 0.05 vs. control; # p < 0.05 vs. glutamate-treated cells, Wilcoxon matched pairs test. For morphometric analysis of synaptophysin immunostaining, at least eight fields were captured for each culture. The density of synaptic puncta was measured as synaptophysin-positive area in each selected field, applying the same threshold parameters to all images. Values were pooled to obtain a single mean value for each condition. Significantly lower positivity for synaptophysin is observed after glutamate treatment. The decrease is reversed in the presence of citicoline (C). * p < 0.05, Mann-Whitney U test. In (D), representative images are shown (syp, red). Bars = 20 μm.