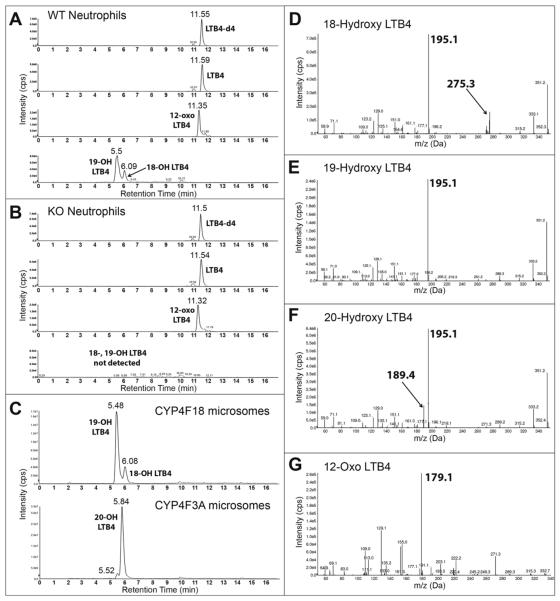
Fig. 3.
LC-MS/MS analysis of LTB4-treated neutrophils.
Bone marrow neutrophils from wild-type mice (A), or Cyp4f18−/− (KO) mice (B), were incubated with LTB4 and extracted and analyzed by LC-MS/MS. Recombinant CYP4F18 and CYP4F3A microsomes, which generate known products of LTB4, were used as controls (C). HPLC chromatogram traces show detection of LTB4 (non-metabolized), 12-oxo LTB4 (product of 12-hydroxydehydrogenase metabolism), and 18-, 19, and 20-hydroxy LTB4 (products of CYP-dependent metabolism). LTB4-d4 was used as an internal standard. MS/MS spectra are shown for the metabolites with retention times of 6.08 min (D, 18-hydroxy LTB4), 5.5 min (E, 19, hydroxyl LTB4), 5.84 min (F, 20-hydroxy LTB4), and 11.35 min (G, 12-oxo LTB4). Characteristic fragments are observed at m/z 195 for all hydroxy LTB4 metabolites, and at m/z 179 for 12-oxo LTB4. Unique fragments are observed for 18-hydroxy LTB4 (m/z 275) and 20-hydroxy LTB4 (m/z 189), as indicated.