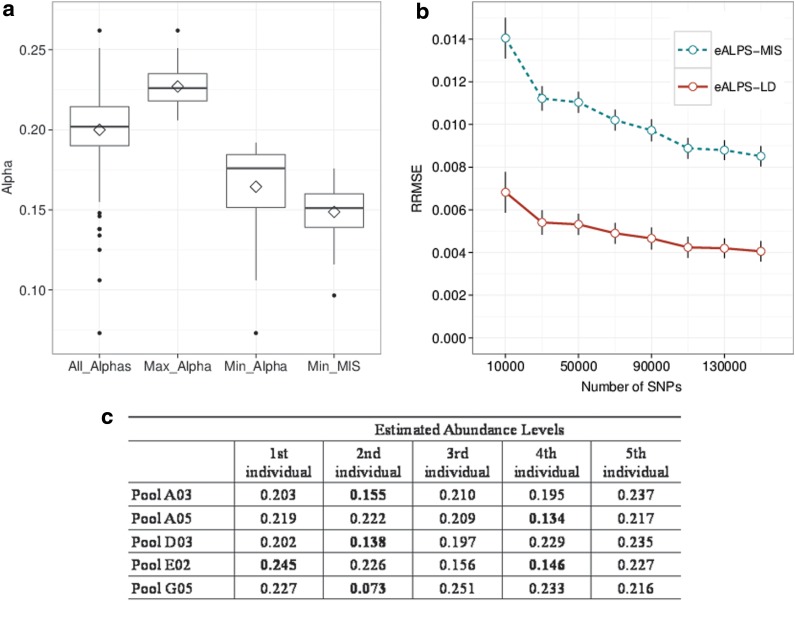
FIG. 2.
Relative abundances in individuals from the NHL study, estimated using eALPS, eALPS-LD, and eALPS-MIS. All pools contain five individuals and were intended to have uniform relative abundances. Panel (a) summarizes the distribution of alphas estimate using eALPS on the NHL data, demonstrating that in practice relative abundances vary. The blue boxplots are (from left to right): all relative abundances, the maximal and minimal abundances for every pool, estimates using eALPS. The red boxplot is the minimal relative abundance estimated by eALPS-MIS, showing that the method systematically underestimates the relative abundance of the missing genotype (minimal values were always achieved for the missing individual). Panel (b) compares the error on the NHL data with one masked genotype as a function of the number of SNPs used in the analysis. The error rates were calculated with respect to the estimated abundance levels obtained from the eALPs method that was given the full genotype data. Panel (c) shows pools with extreme relative abundances. NHP, non-Hodgkins's lymphona.