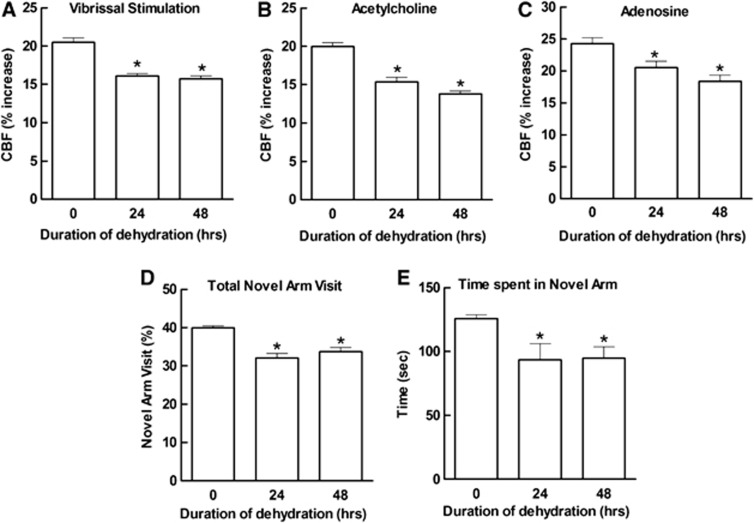
Figure 2.
Dehydration impairs cerebral blood flow (CBF) responses induced by neural activity, and by the endothelium-dependent vasodilator acetylcholine (ACh) or the smooth muscle relaxant adenosine (A–C). Dehydration impairs cognitive function assessed by the Y maze test. Both the number of visits to the novel arm and the time spent in the novel arm were reduced in dehydrated mice (D, E). Data are normalized by the total arm visits to the three arms (see Materials and methods). *P<0.05 versus vehicle (0 hour); analysis of variance and Tukey's test; n=15/group.