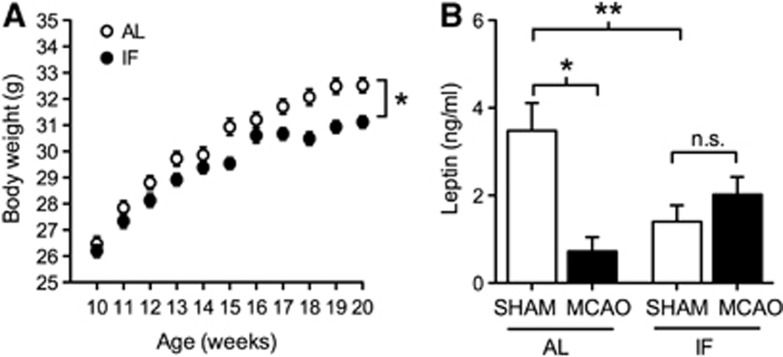
Figure 1.
Intermittent fasting (IF) reduces body weight and prevents stroke-induced reductions in circulating leptin levels. (A) Weight gain is reduced in mice exposed to IF on a 16:8 hours fasting and refeeding schedule. Asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance at P<0.05 after repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA). (B) Stroke dramatically reduces circulating leptin levels in mice on the ad libitum diet, but not in mice maintained on IF. Asterisk (*, **) indicates statistical significance at P<0.05 (*) or P<0.01 (**) following 2 × 2 ANOVA. Leptin levels were assessed 3 days after middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) or sham operation and error bars represent the s.e.m. AL, ad libitum.