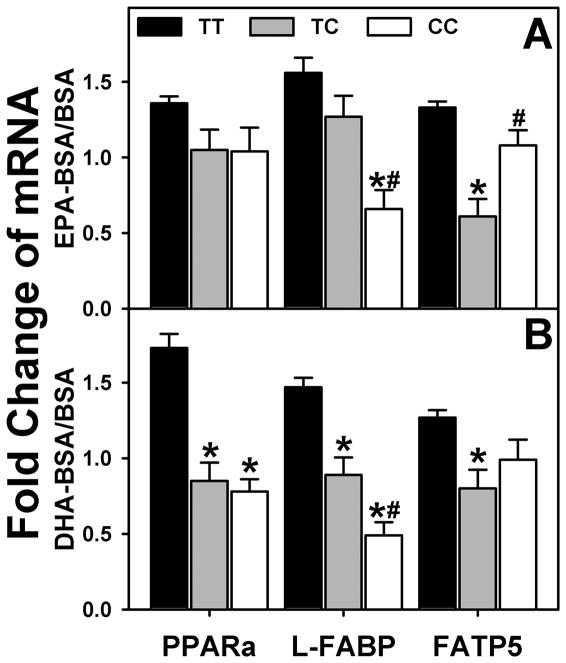
Figure 9. Effect of human L-FABP T94A mutation on ligand-induced transcription of PPARα-regulated proteins.
Primary human hepatocytes were cultured overnight, and then incubated for 24h with fatty acid-free BSA (Alb) or EPA/BSA, or DHA/BSA (200 μM EPA or DHA) in 6 mM glucose-containing medium as we described in Experimental Procedures. rtPCR was used to determine human PPARα, L-FABP, and FATP5 mRNA levels normalized to an internal control (18S RNA). Values presented were the fold change induced by BSA/EPA or BSA/DHA complex relative to BSA only. Mean ± SEM, n=8–10 different samples in each group, *p<0.05, homozygous T94A (CC) and heterozygous (TC) variants were compared to wild-type (TT); #p<0.05, homozygous T94A (CC) were compared to heterozygous (TC) variants.