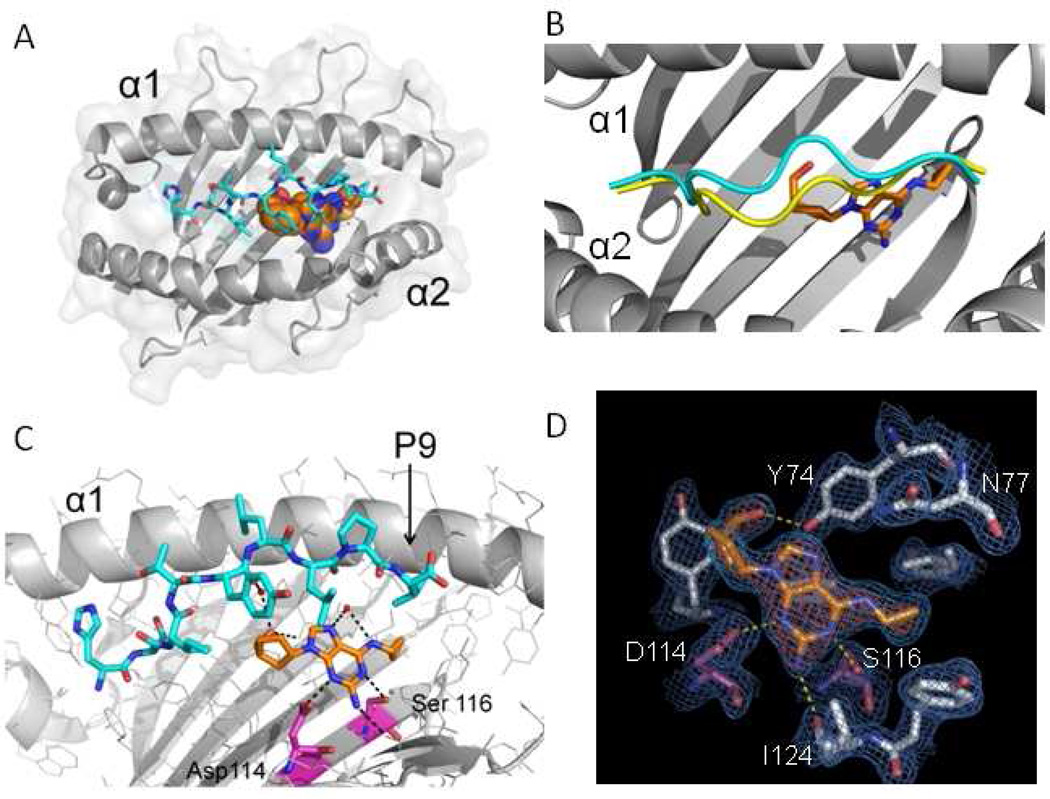
Figure 1.
The altered peptide repertoire model of abacavir hypersensitivity. Crystal structure of the abacavir-MHC-peptide complex shown to resolution of 0.2 nm (nanometers). a HLA-B*57:01 is shown in gray, peptide V is shown in cyan, and abacavir is shown as a multicolored structure (spheres with orange for carbon, blue for nitrogen, and red for oxygen). b Abacavir binding leads to altered peptide repertoire by changing the conformation of the peptide backbone in the main chain of HLA-B*57:01. Binding of peptide is shown in the absence of abacavir (yellow) and associated with abacavir and HLA-B*57:01 (cyan). c H-bound interactions (black dashes) are shown between abacavir, peptide, and HLA-B*57:01. Specific residues differentiating for abacavir-sensitive HLA-B*57:01 from abacavir-insensitive HLA-B*57:03 are shown in magenta (carbon), blue (nitrogen), and red (oxygen). d Experimental electron density showing abacavir in a Fo-Fc difference map with blue mesh showing the final 2Fo-Fc electron density map of abacavir in the antigen-binding cleft of HLA-B*57:01. H-bond interactions between abacavir and HLA-B*57:01 are shown in yellow. (Adapted from Ostrov et al. [14])