Figure 4.
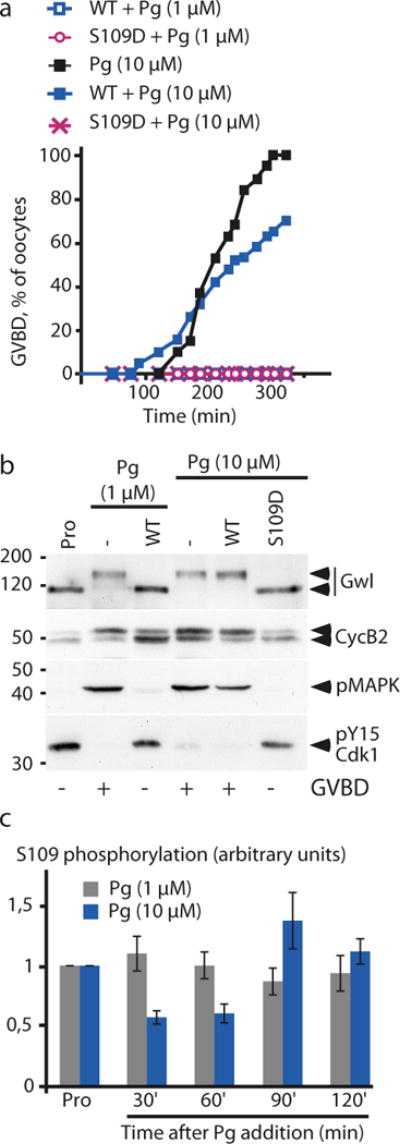
The inhibitory effect of injected WT-GST-ARPP on meiotic resumption depends on the concentration of Pg.
(a) GVBD time course of WT- or S109D-injected oocytes in response to increased concentrations of Pg. Prophase-arrested oocytes (Pro) were injected with 600 ng of either WT- or S109D-ARPP then stimulated with 1 μM of Pg. 16 hours later, no maturation was observed. Injected oocytes were further incubated with 10 μM of Pg in the external media and the GVBD time course was followed.
(b) Increasing the concentration of progesterone promotes Cdk1 activation in WT-GST-ARPP injected oocytes. Prophase-arrested oocytes (Pro) or Pg-treated oocytes (Pg) from panel (a) were collected 16 hours after 1 μM Pg stimulation or at time of GVBD in response to 10 μM Pg. Oocytes were analyzed by immunoblotting Gwl, Cyclin B2 (CycB2) upshift, phosphorylated MAPK (pMAPK) and Cdk1 phosphorylation at Y15 (pY15-Cdk1).
(c) The extent of ARPP19 dephosphorylation at S109 depends on Pg concentration. Prophase-arrested oocytes were injected with 600 ng of WT-GST-ARPP then induced to mature either with 1 μM or 10 μM of Pg. Oocytes were collected after Pg addition at the indicated times. The phosphorylation at S109 and the total amount of WT-GST-ARPP were immunoblotted using a specific phospho-S109 and a GST antibody respectively. S109 phosphorylation level of ARPP19 was further quantified using ImageJ software (n=6). The error bars represent means ± s.e.m.
