Figure 5. IL-6 is crucial for S1P1-mediated STAT3 activation.
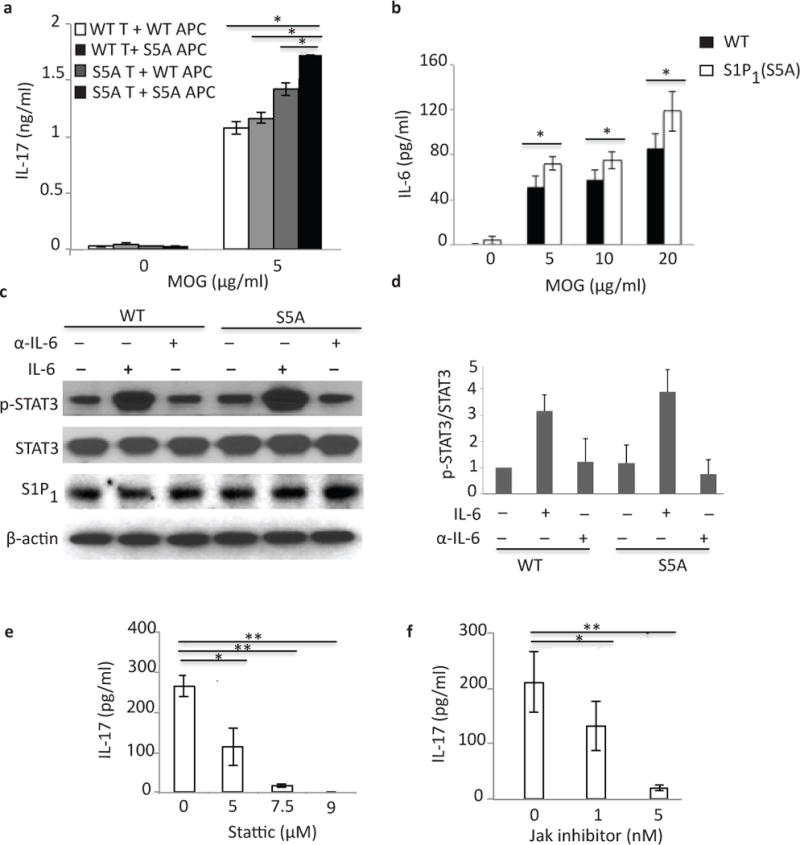
(a) IL-17 expression in culture supernatants of mixed lymphocyte cultures [CD3+ cells from MOG35–55-immunized S1P1(S5A) (S5A T) or C57BL/6J WT (WT T) EAE mice co-cultured with naïve, irradiated antigen presenting cells (APCs)from S1P1(S5A) (S5A APC) or WT (WT APC) in the presence of MOG35–55 peptide] measured by ELISA. (b) IL-6 expression in an ex vivo recall assay of splenocyte cultures from MOG35–55-imunized S5A [S1P1(S5A)]and WT EAE mice (day 8 post-immunization). (c) Immunoblot depicting p-STAT3 expression in splenocytes from WT and S1P1(S5A) EAE mice (day 8 post-immunization) treated in vitro with recombinant IL-6 (IL-6) or anti-IL-6 (α-IL-6) (20ng/ml, respectively). (d) Quantification of normalized p-STAT3 expression from (c). IL-17 expression in the culture supernatants of splenocyte cultures from MOG35–55-immunized S1P1(S5A) mice treated in vitro with Stattic (STAT3 inhibitor) (0–9 μM) (e) or Jak inhibitor (0–5nM)(f). **p<0.01, *p<0.05 by Students t-test. Experiments were performed 3–5 times with n=3–5 mice.
